Vaginal Microscopy Summary Table B
Findings associated with elevated pH (>4.5)
(Highlighted areas indicate increasing abnormalities on the slide, in the setting of elevated pH.)
| MICROSCOPY FINDINGS (Click on “cameras” for photos of slides.) |
POSSIBLE INTERPRETATIONS WHEN PATIENT SYMPTOMATIC | OTHER ACTIONS |
|---|---|---|
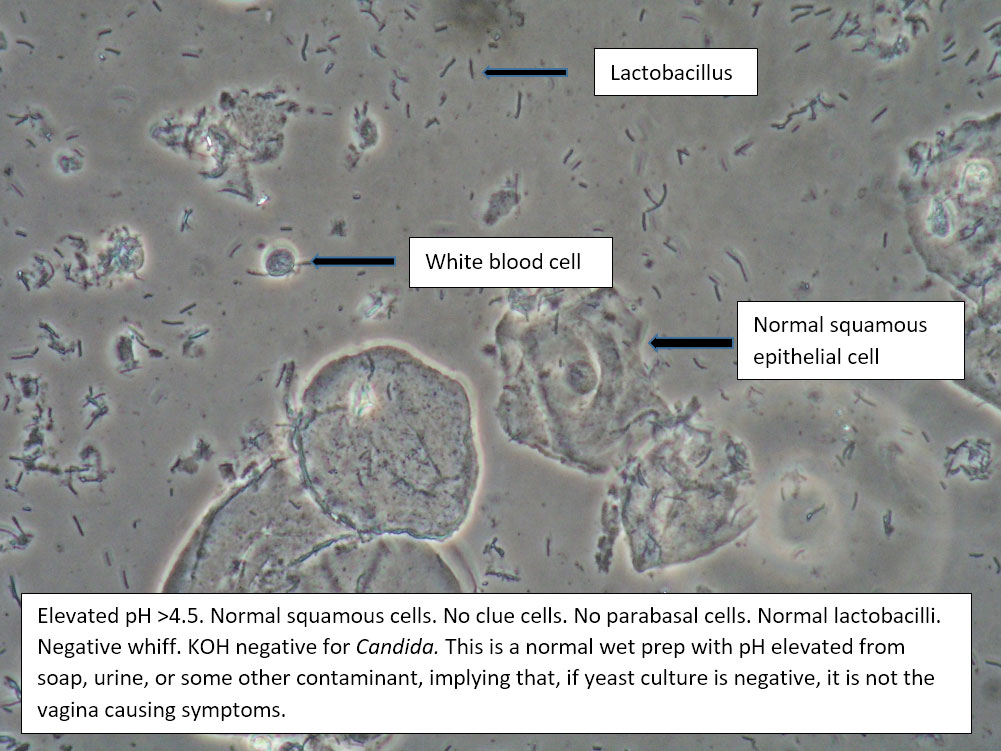
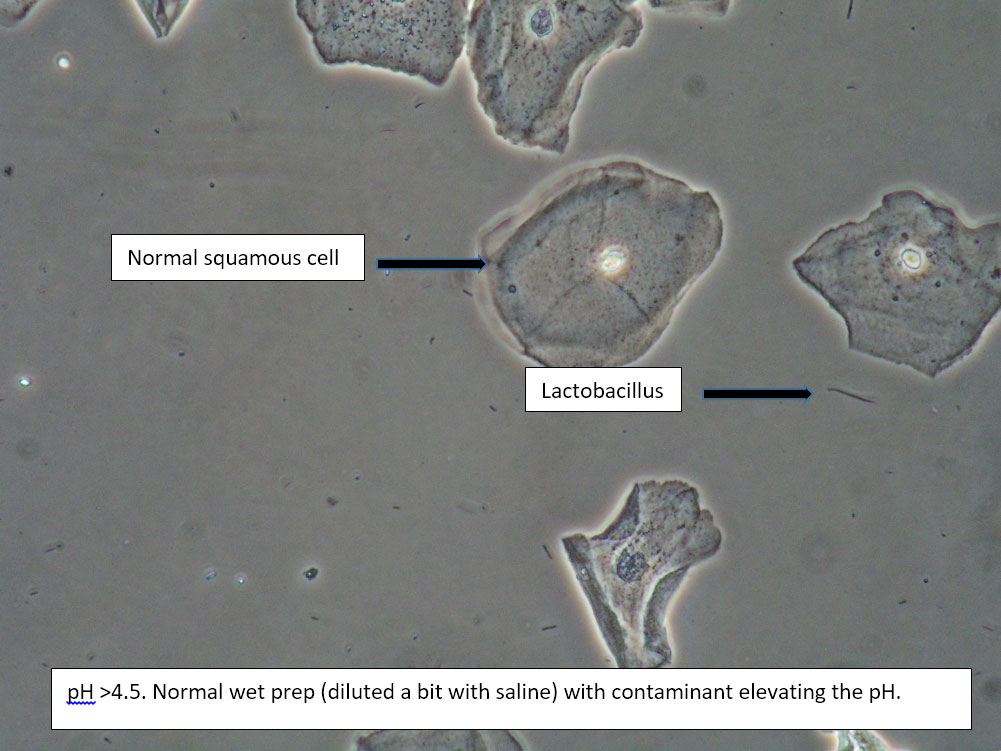
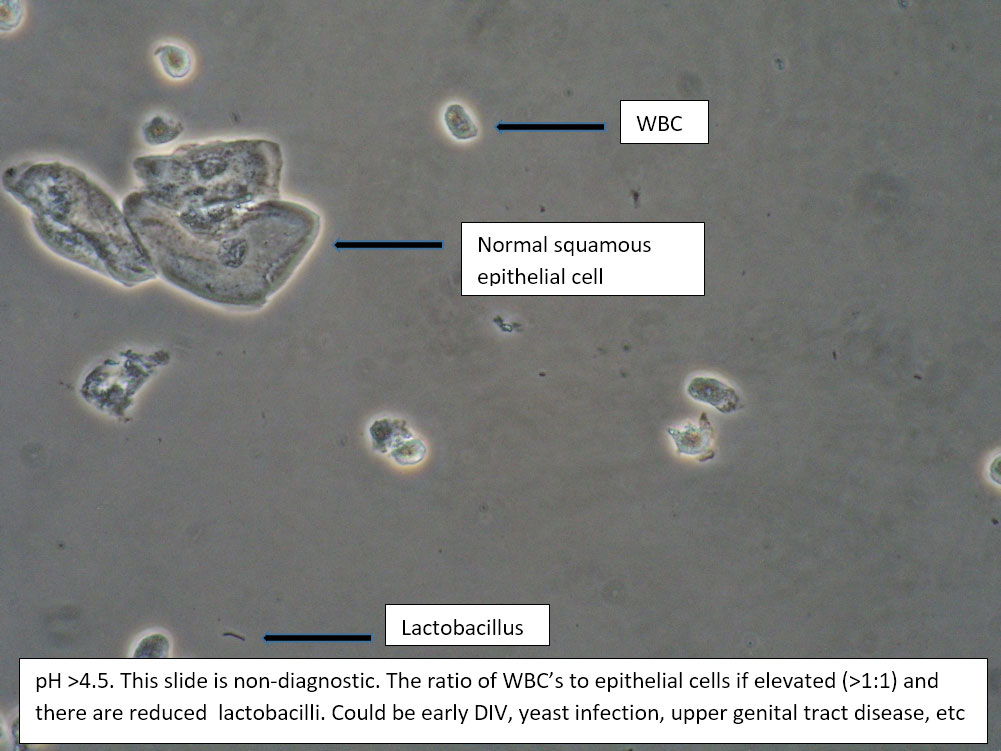
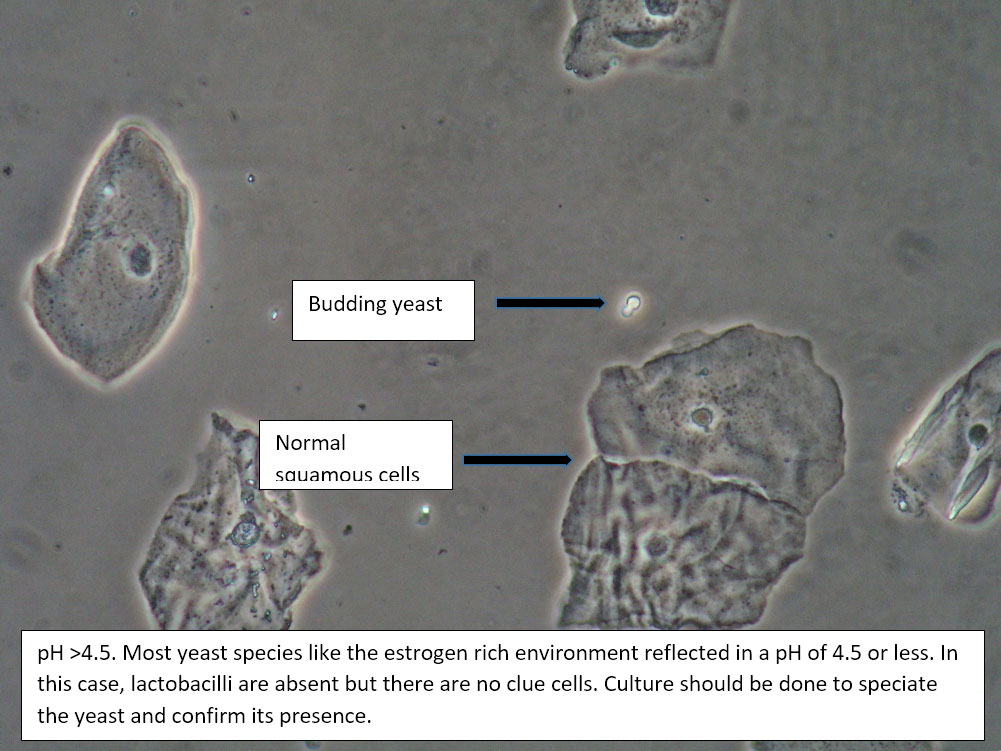
| Box 1: Normal squamous cells No clue cells No parabasal cells 1 WBC per epithelial cell Lactobacilli present Negative whiff KOH negative for Candida |
1) Normal physiological discharge with contamination causing elevated pH (blood, semen, soap, urine, chemicals, etc). Reassure patient. 2) Candida (yeast can be present even when not seen on wet prep) 3) Symptoms may be related to pelvic floor, vulvodynia, or vulvar epithelium. |
This is normal wet prep with elevated pH. Consider that pH may be normally elevated past 4.5 in certain ethnic groups: White (pH 4.2±0.30), Asian (pH 4.4±0.59), Black (pH 4.7±1.04), Hispanic (pH 5.0±074).
Also consider contamination. |
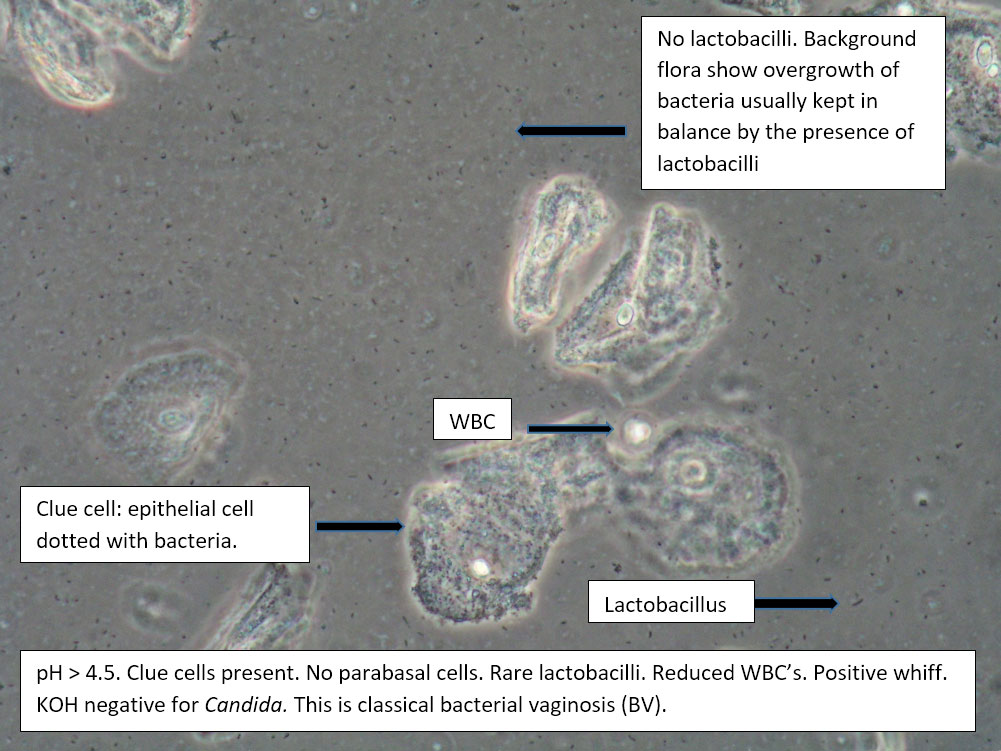
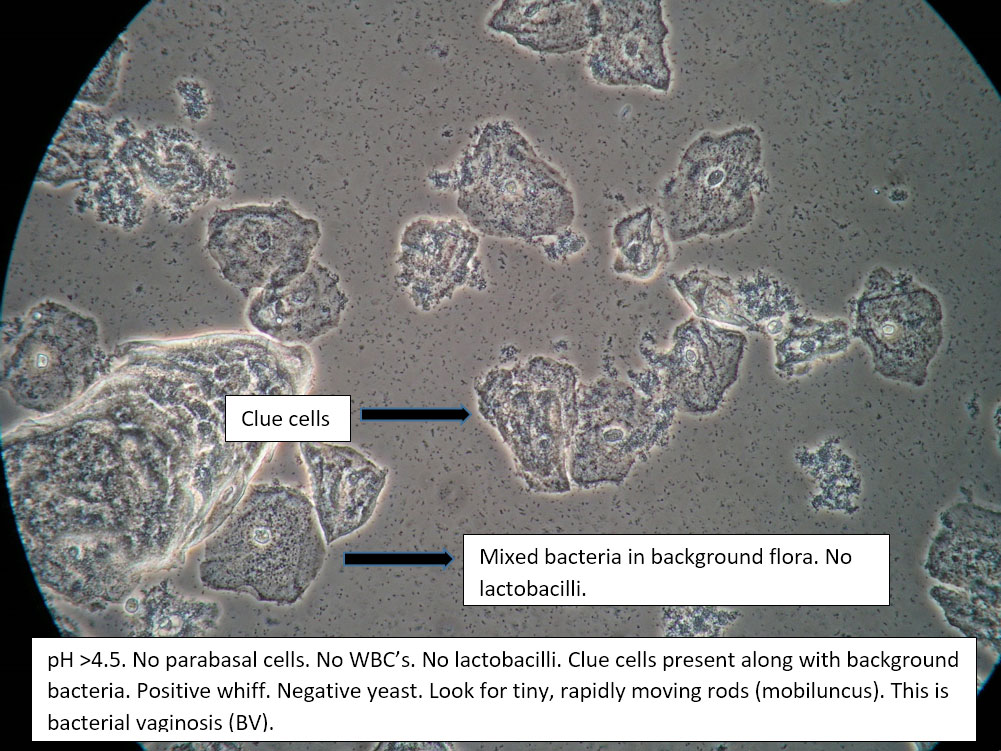
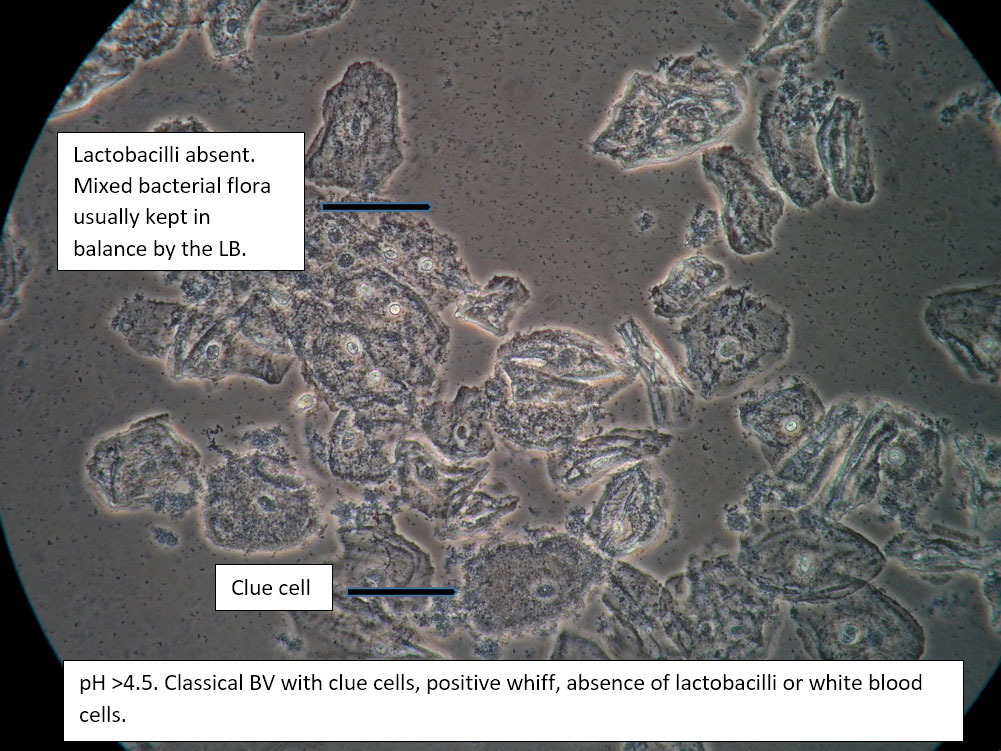
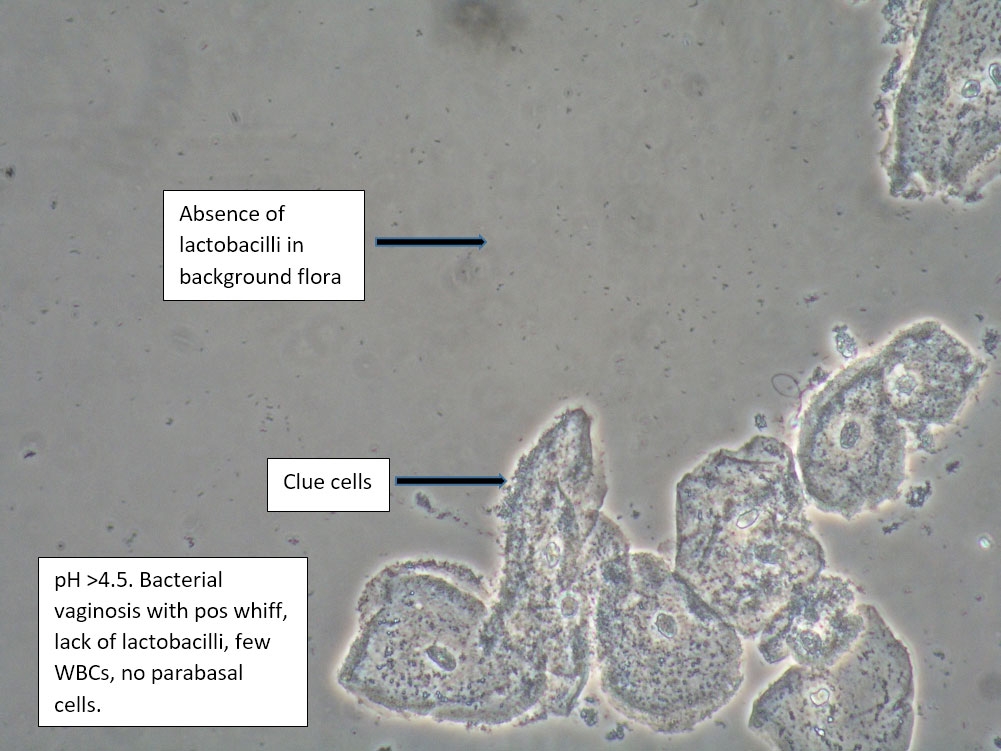
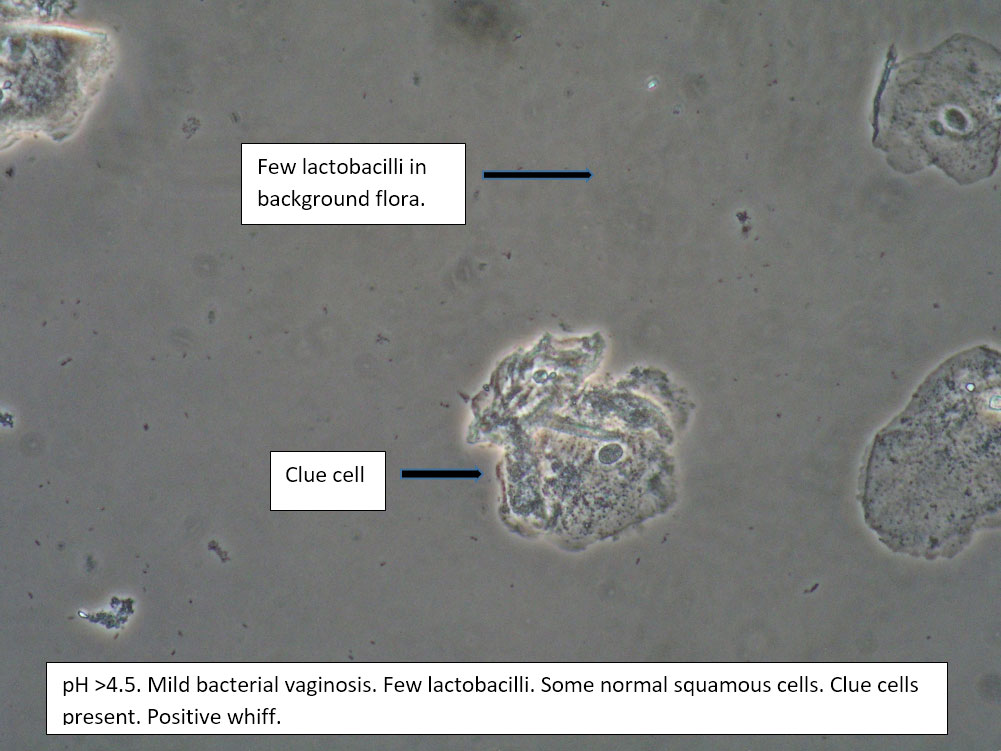
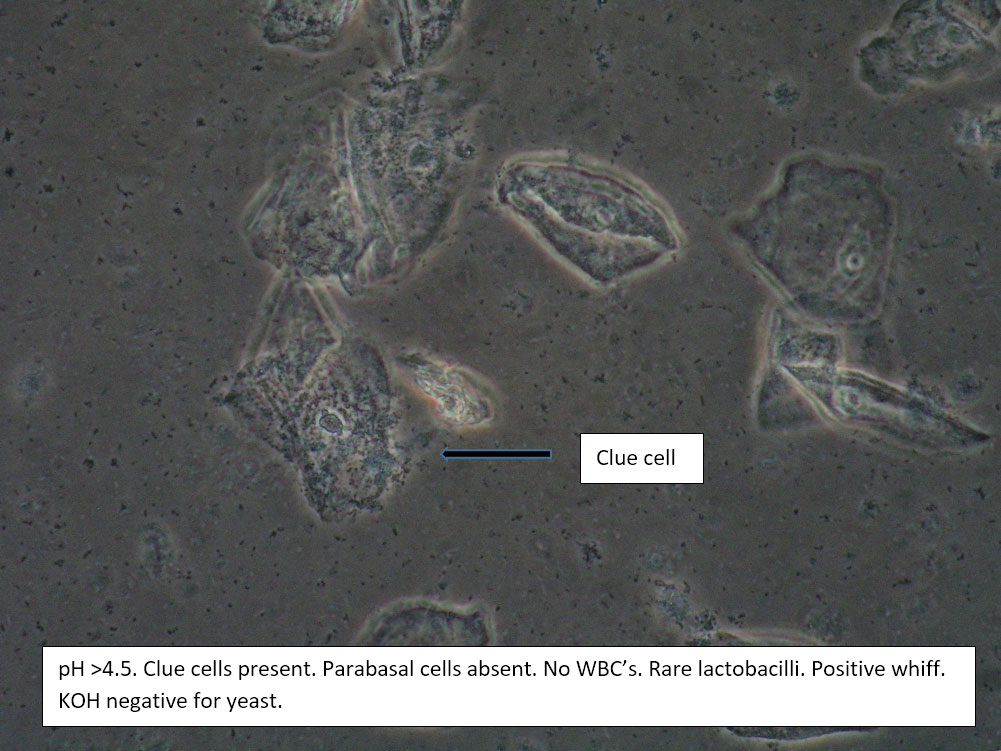
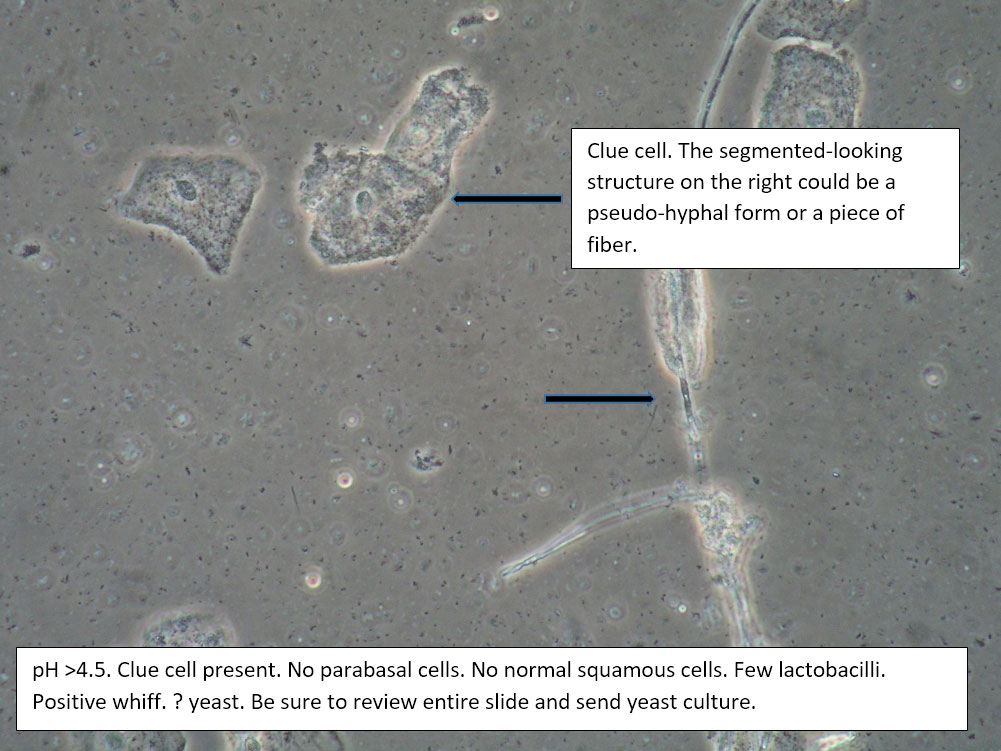
| Box 2: Normal squamous cells Presence of clue cellsNo parabasal cells 0-1 WBC per epithelial cell Lactobacilli reduced or absent Positive whiff |
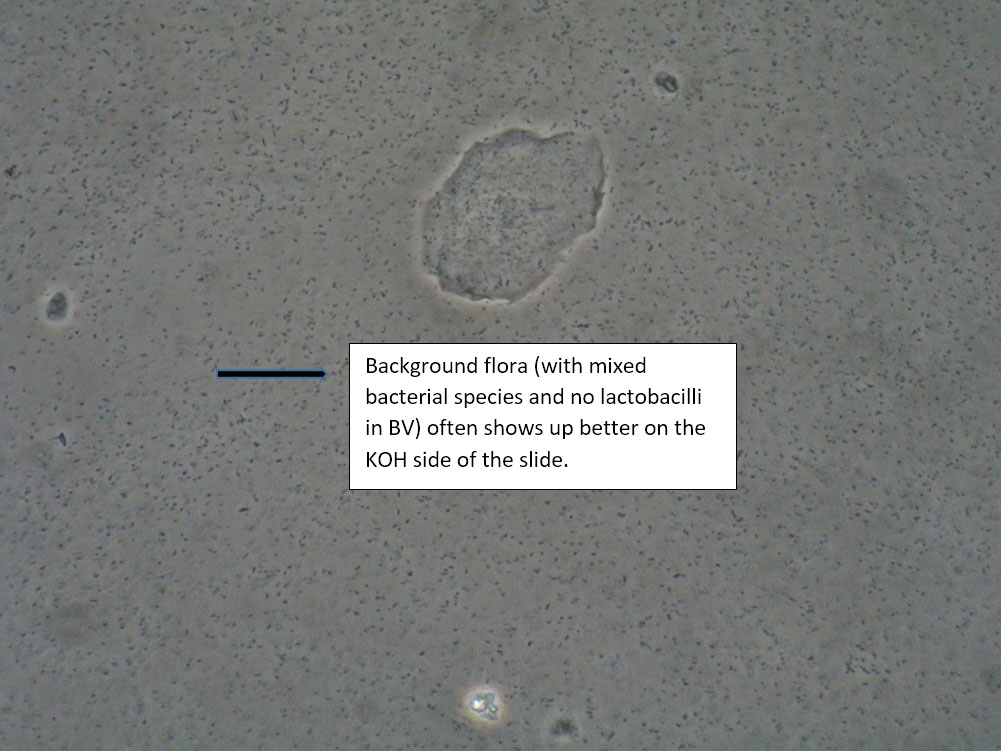
Bacterial vaginosis (see Amsel’s criteria) (Note that WBCs are usually absent with BV) | 1) Look for other background flora (e.g. mobiluncus) Mobiluncus video 2) Yeast culture 3) Treat for and counsel about BV; anticipate yeast infection from antibiotic. 4) Complete Algorithm steps. |
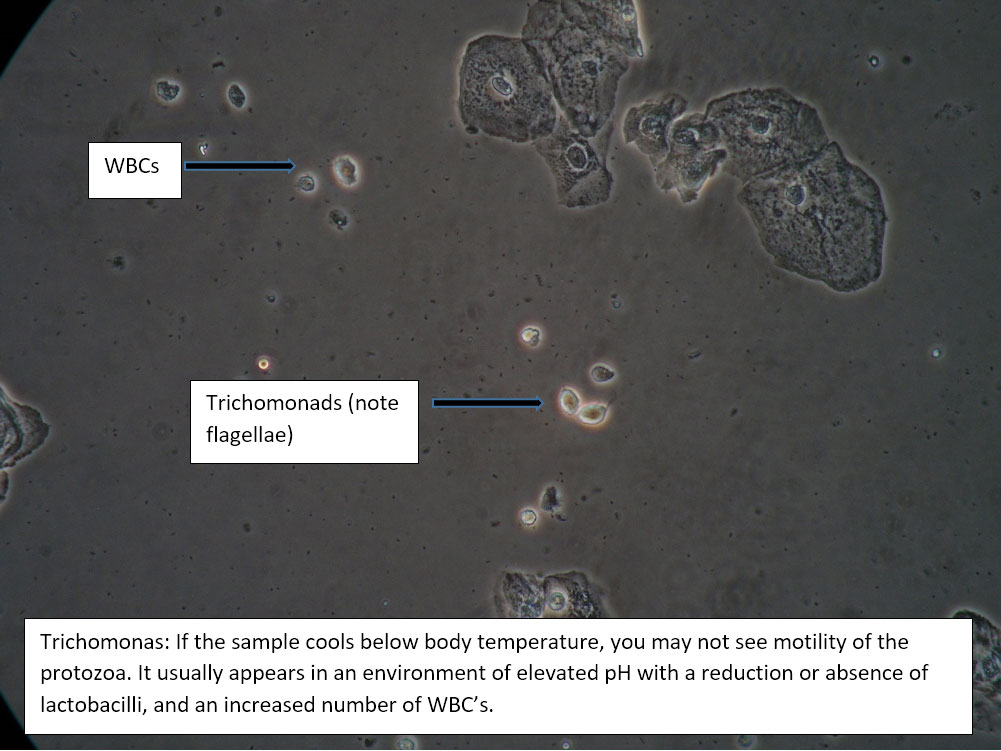
| Box 3: Normal squamous cells No clue cells No or rare parabasal cells >1 WBC per epithelial cell Lactobacilli reduced or absent Presence of motile trichomonads Trichomonas video Negative whiff KOH negative for Candida |
Trichomonas | 1) Adjuvant test for trichomonas if necessary, 2) Yeast culture. 3) Treat and counsel for trichomoniasis; anticipate yeast infection from antibiotic. 4) Complete Algorithm steps. |
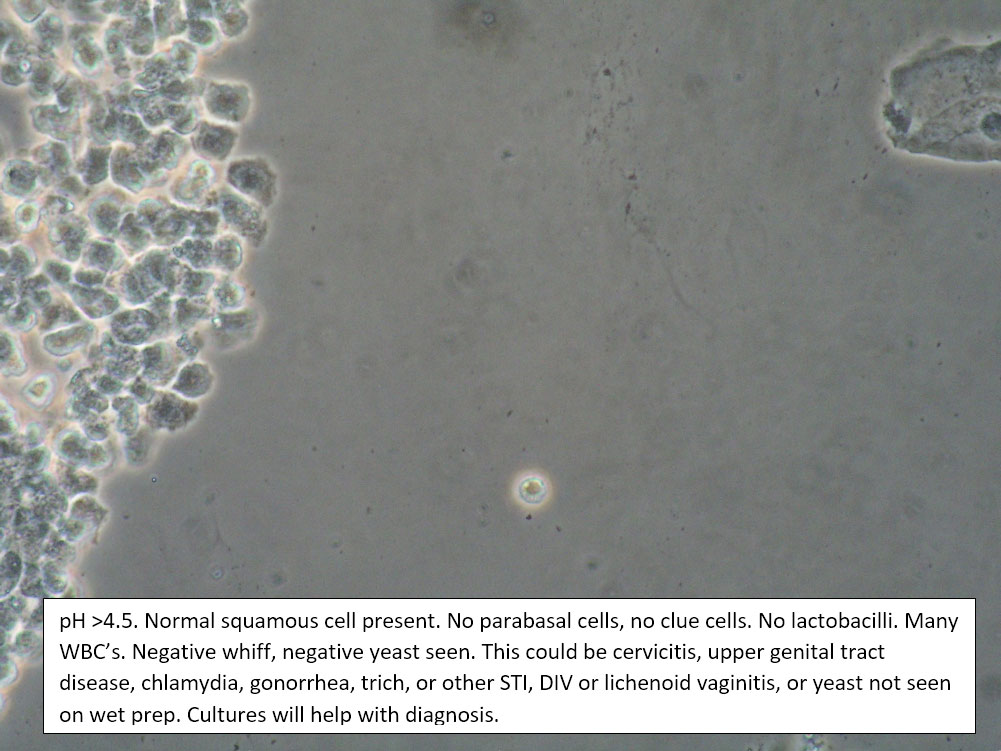
| Box 4: Normal squamous cells No clue cells No or rare parabasal cells >1 WBC per epithelial cell Lactobacilli reducedTrichomonads absent Negative whiff KOH negative for Candida |
1) Possible Trichomonas 2) Cervicitis 3) Chlamydia, gonorrhea 4) Upper genital tract disease (cervical, uterine, tubal, pelvic inflammation) 5) Fistula6) Candida (Yeast can be present even when not seen on wet prep) |
1) Look for motile trichomonads. 2) Adjuvant test for trichomonas. 3) Yeast culture. 4) Look for cervical inflammation and friability with discharge, in which case, test for GC/Chlamydia, Pap. 5) Evaluate for upper tract disease. 6) Evaluate for fistula. 7) Complete Algorithm steps. |
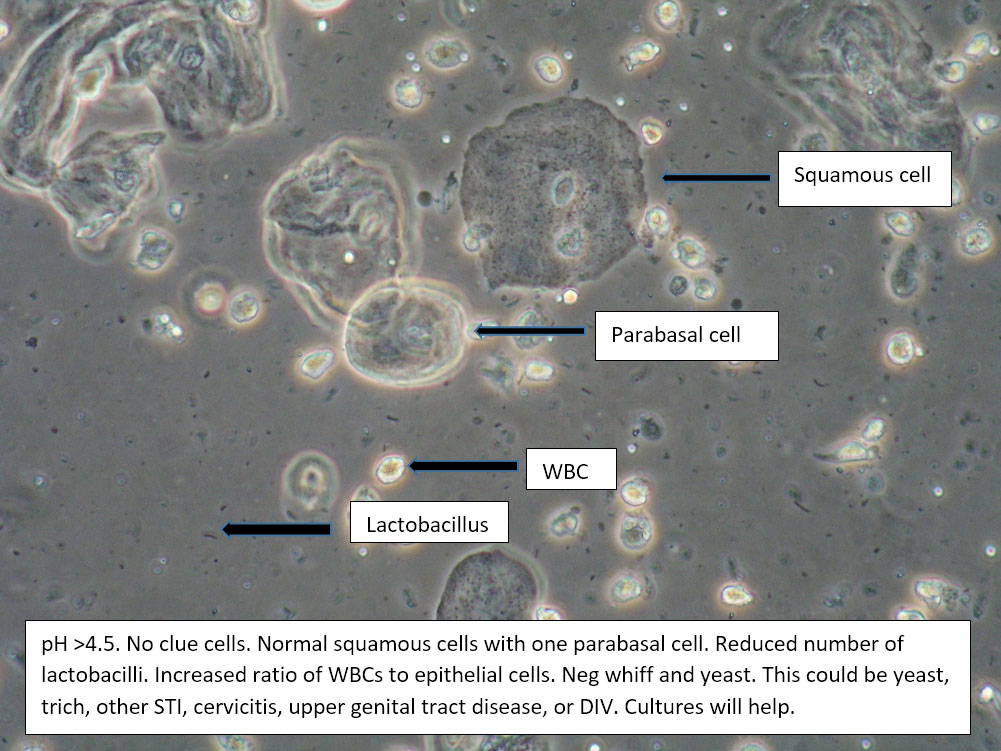
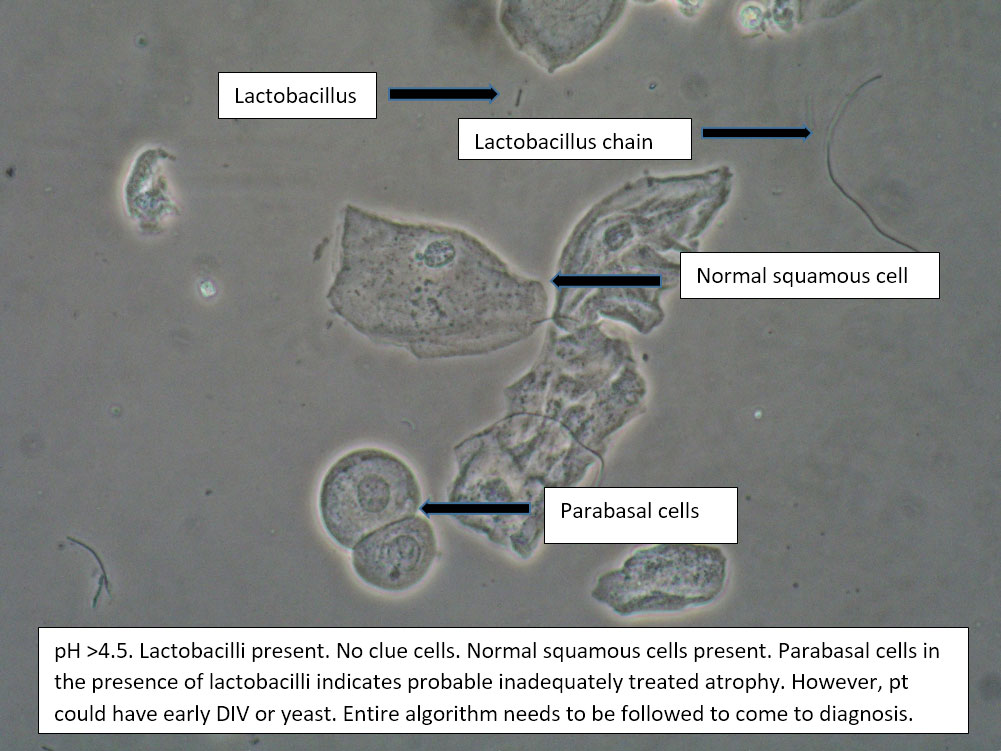
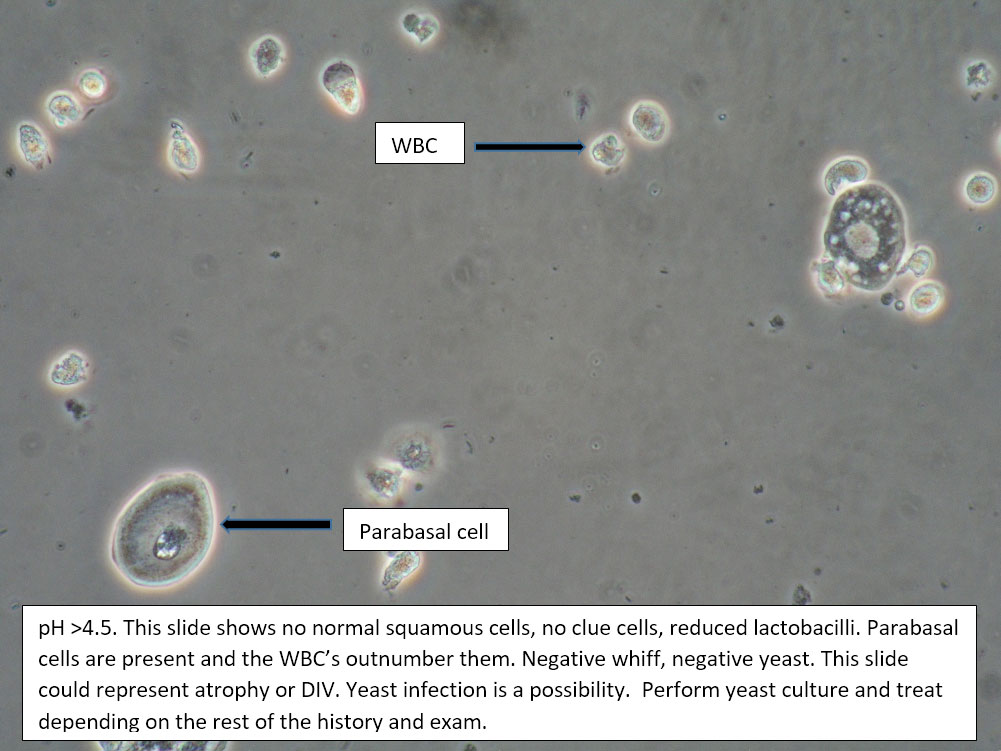
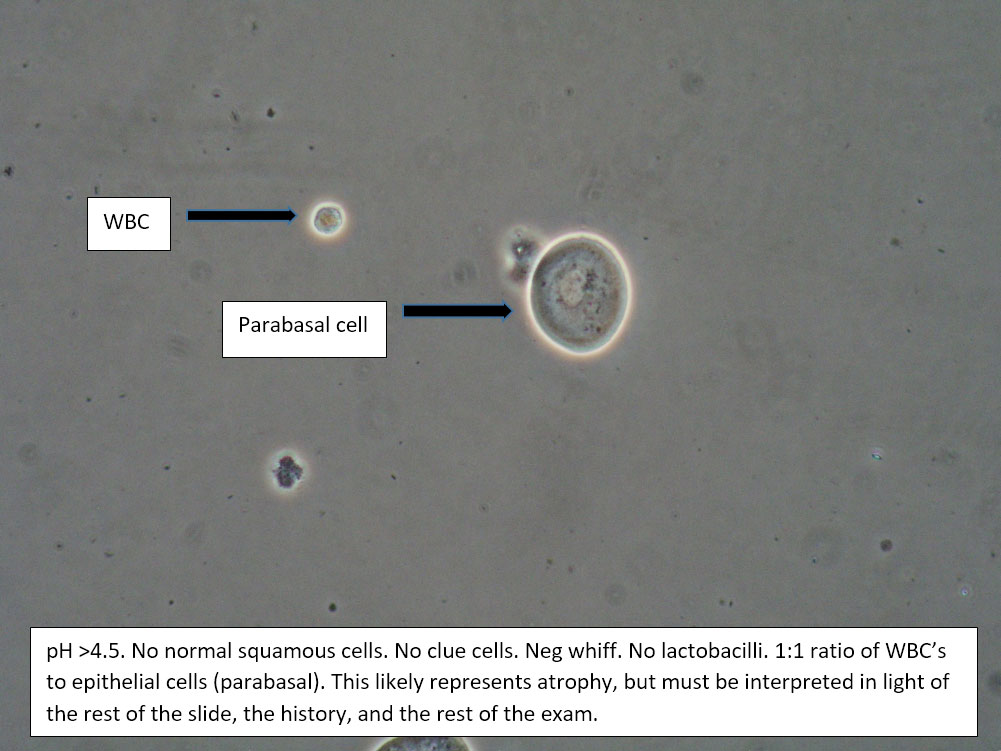
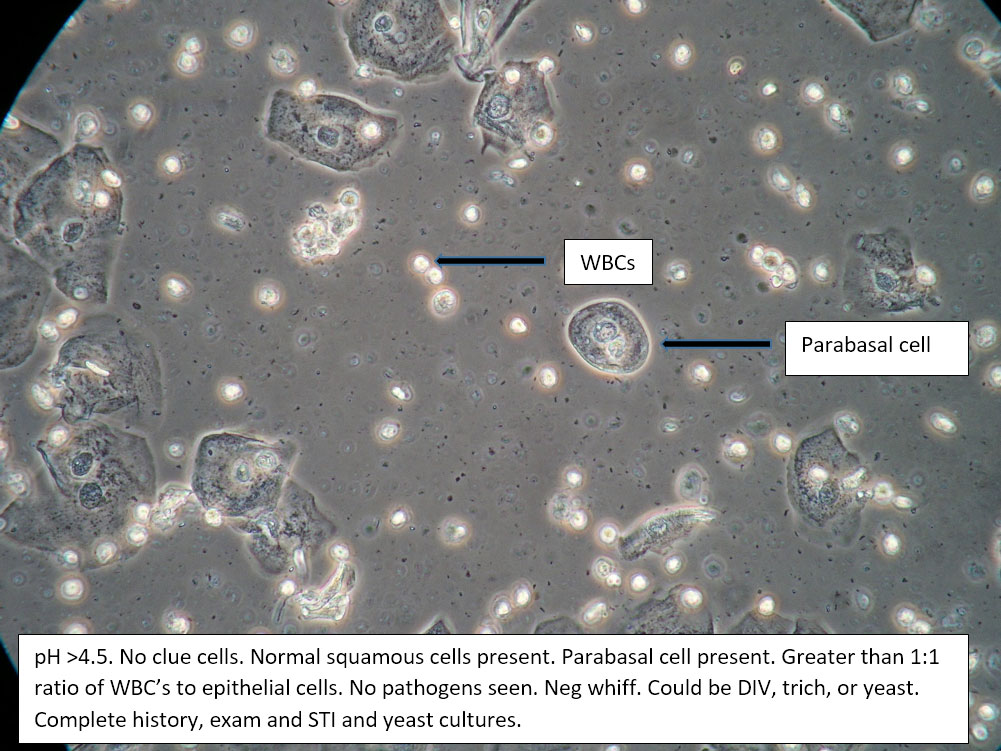
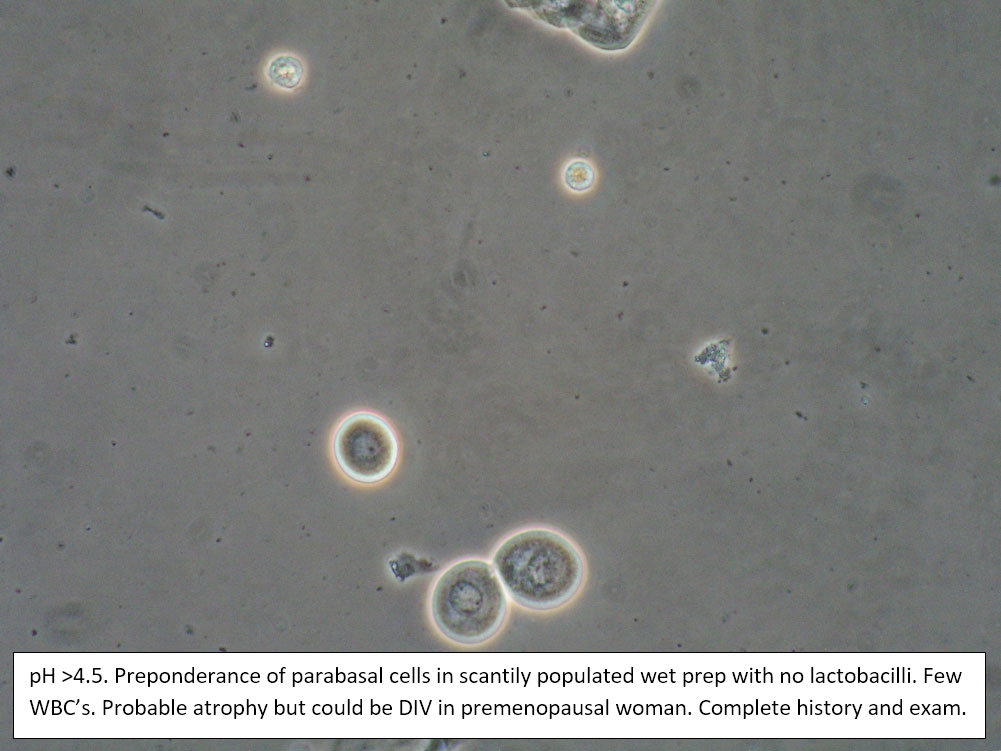
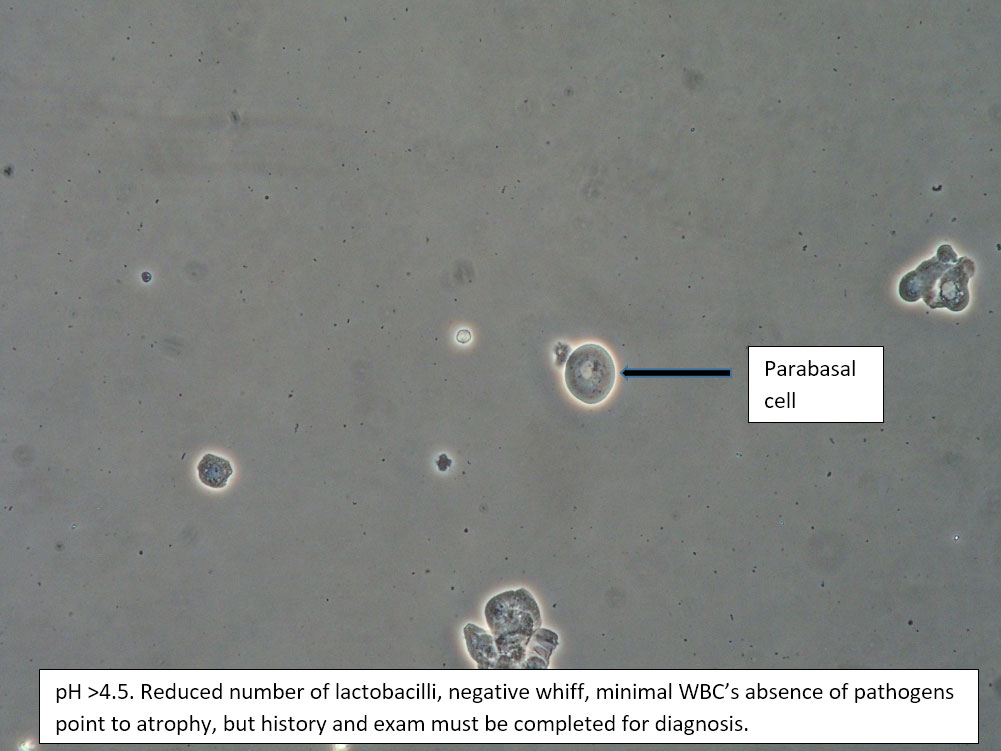
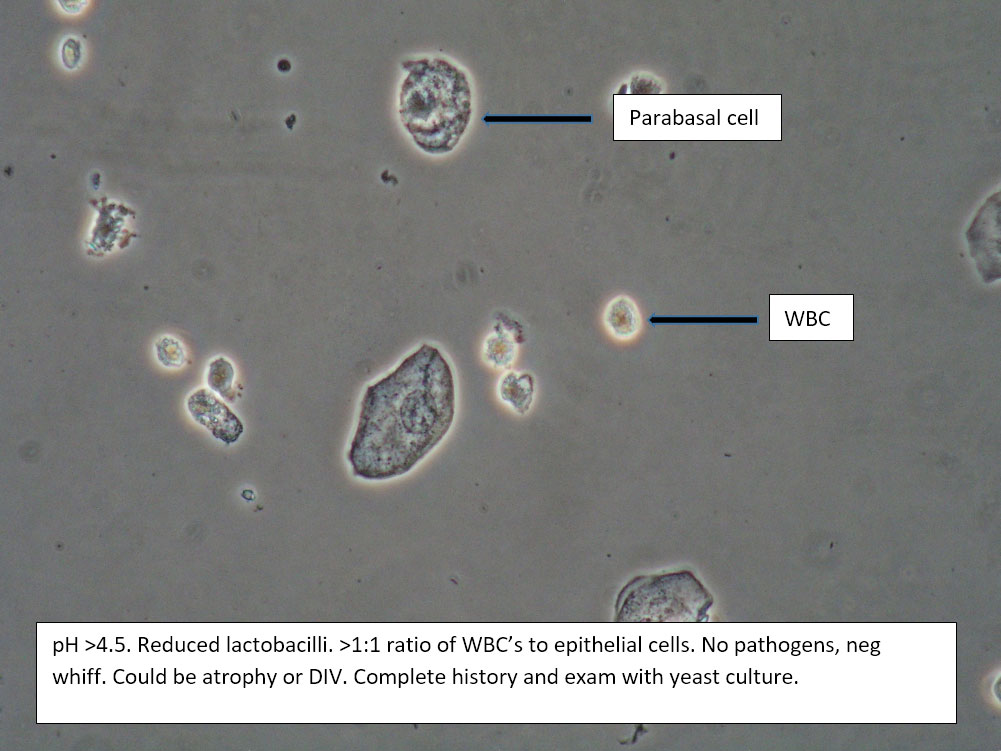
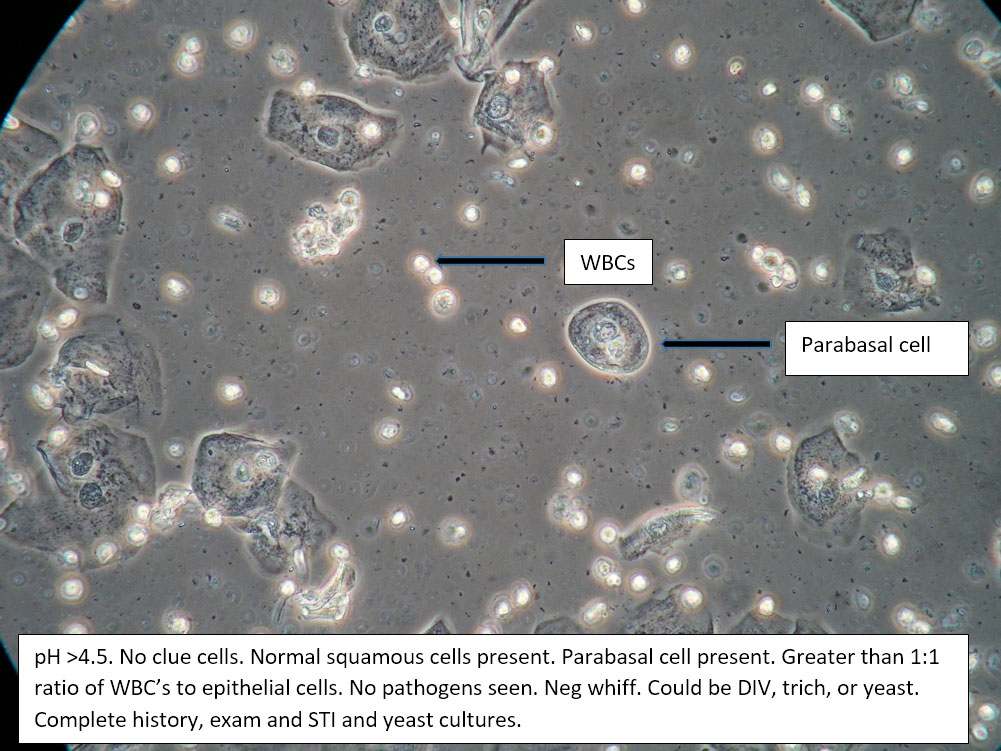
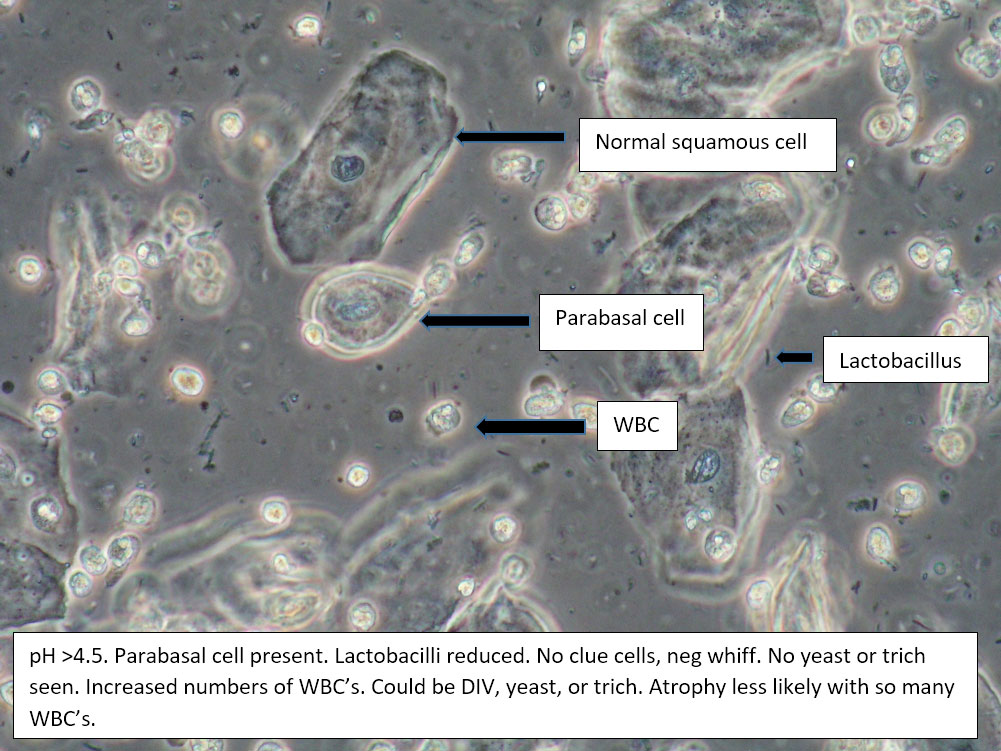
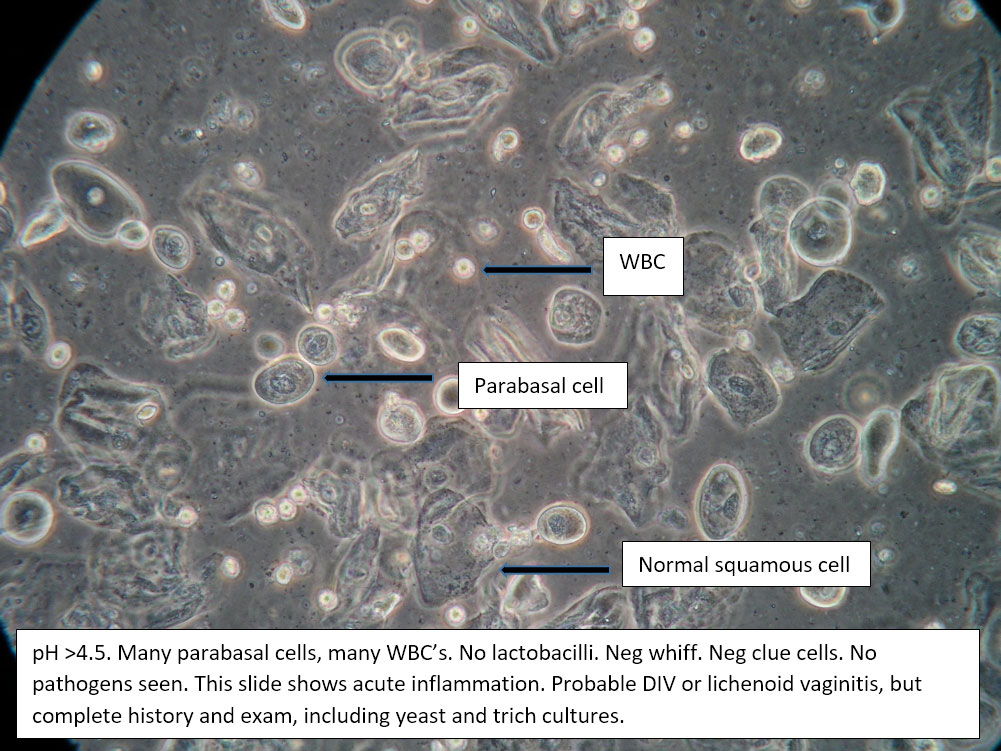
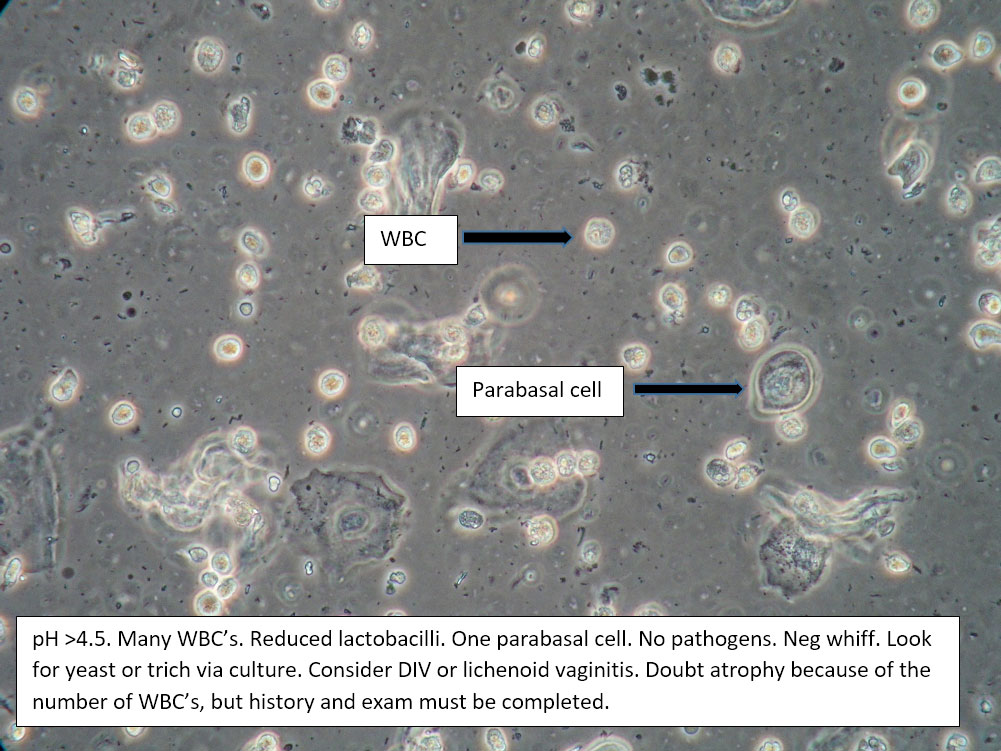
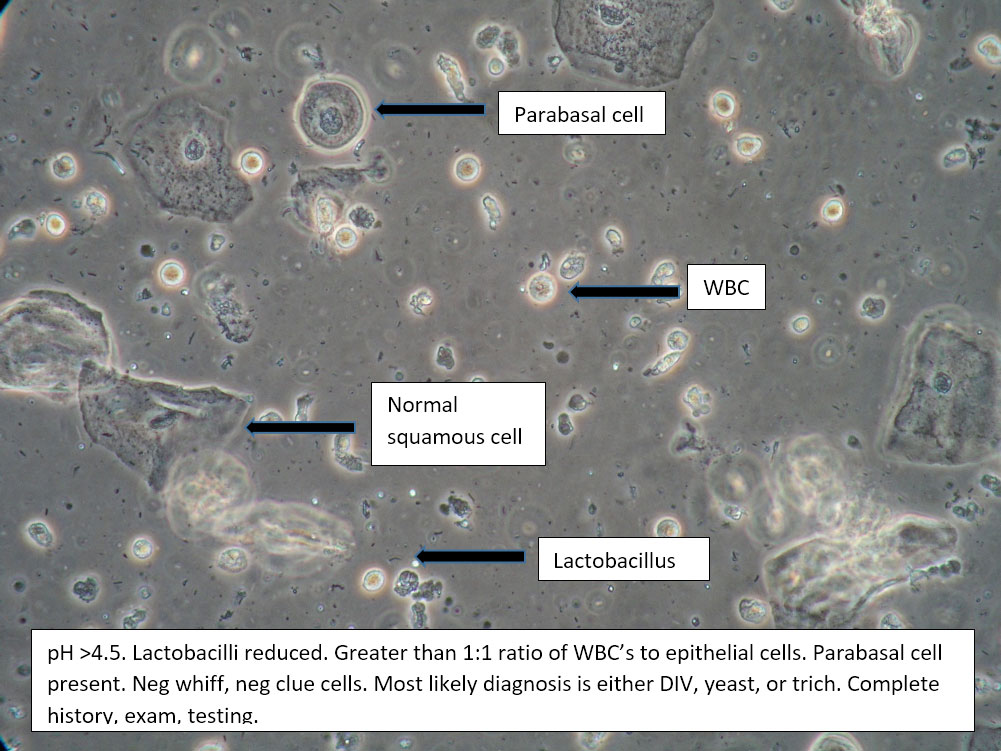
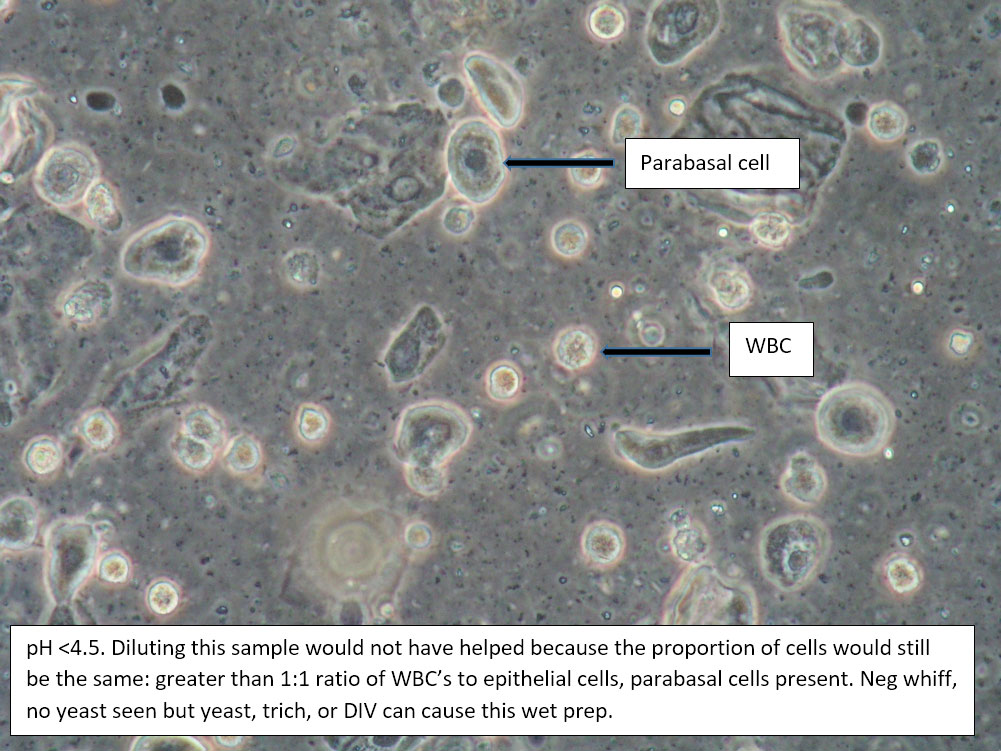
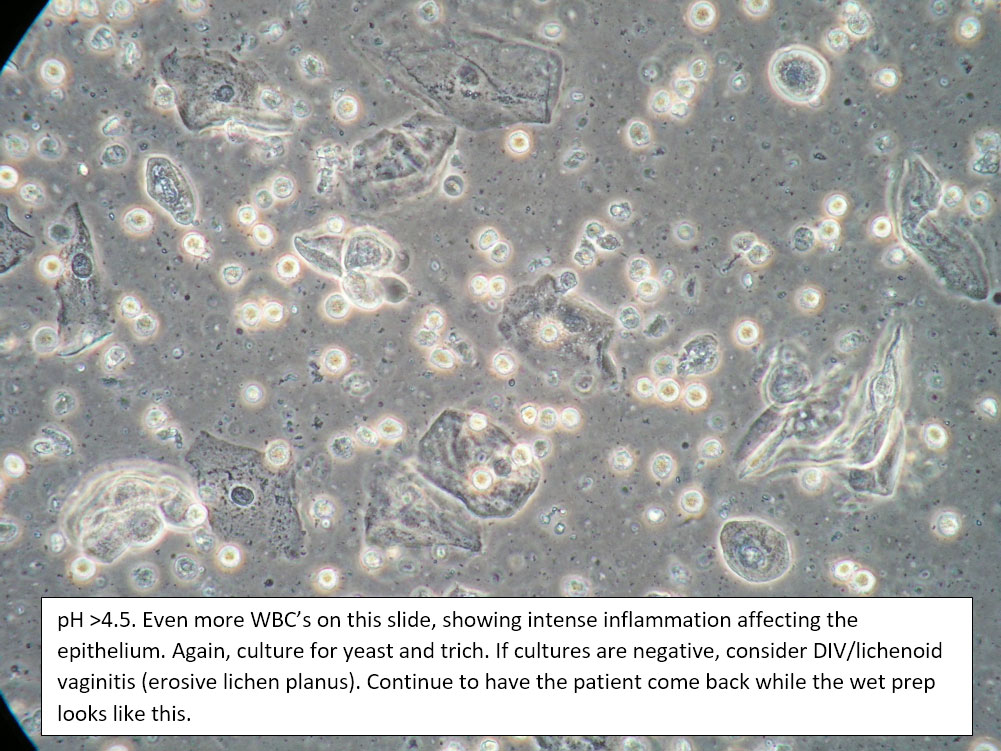
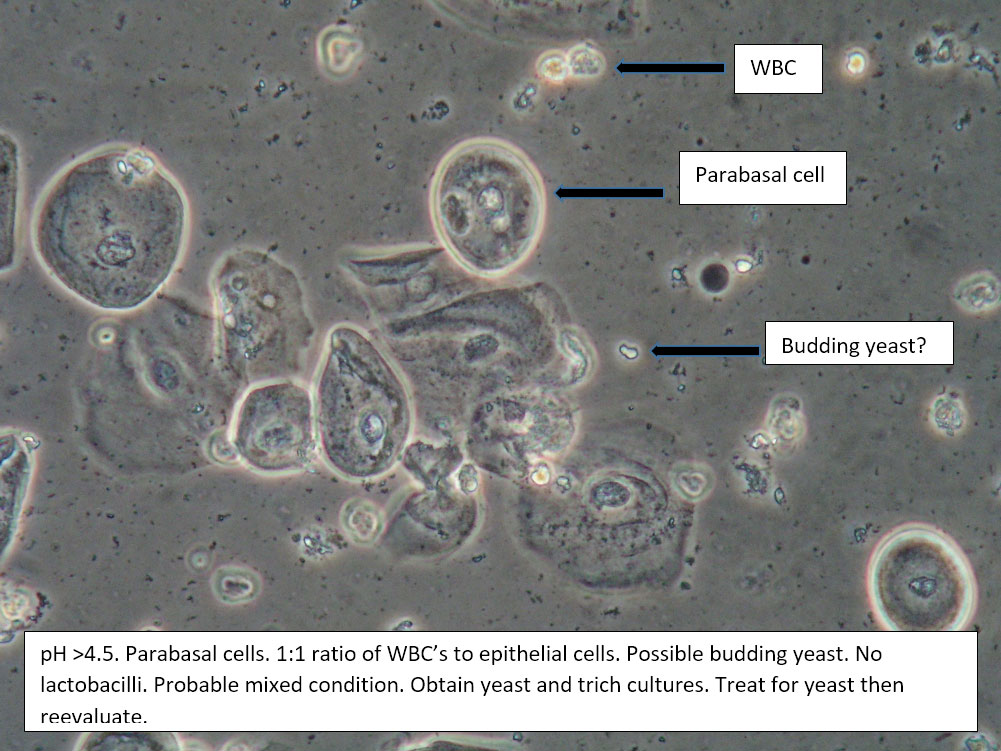
| Box 5: Some or no normal squamous cells No clue cells Parabasal cells present 1->1 WBC per epithelial cell Lactobacilli reduced or absent Trichomonads absent Negative whiff KOH negative for Candida |
1) Atrophy 2) Inflammatory vaginitis (DIV) or erosive lichen planus (LP) 3) Candida (yeast can be present even when not seen on wet prep) 4) Trichomonas possible(See photos for more hints about diagnosis.) |
1) Yeast culture 2) FSH if appropriate 3) Treat for atrophy in post-menopausal women, then re-evaluate for correction in symptoms and wet prep. If not improved, consider DIV. 4) In premenopausal women, wait for yeast culture; treat for DIV or LP if yeast culture negative. 5) Test for trichomonas.6) STI testing is always appropriate. 7) Complete Algorithm steps. |
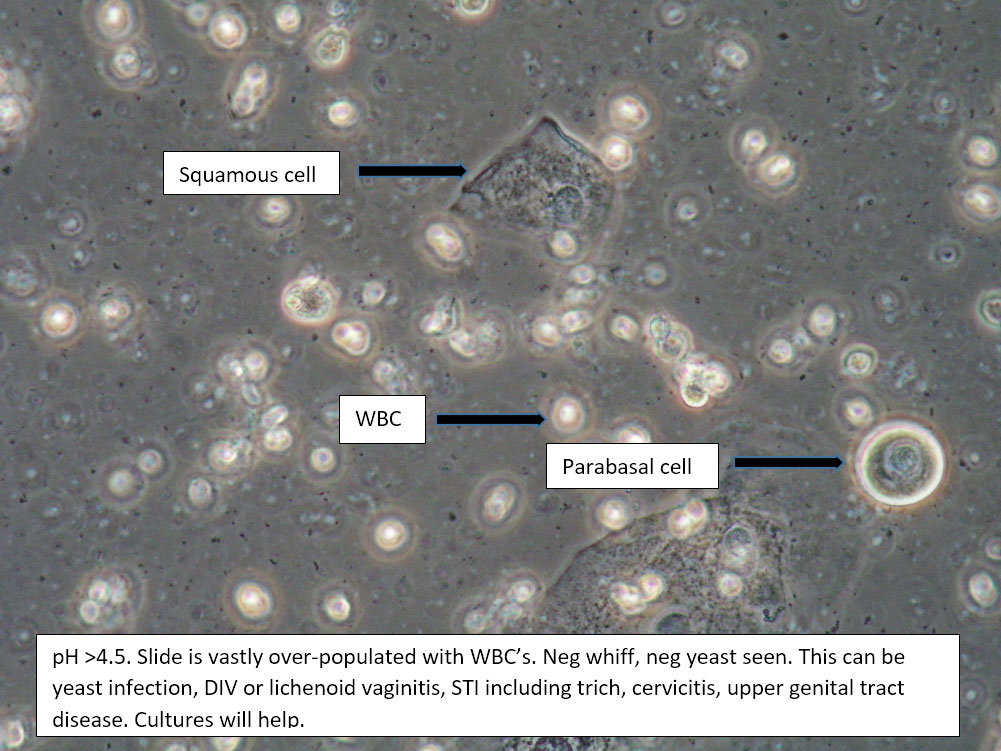
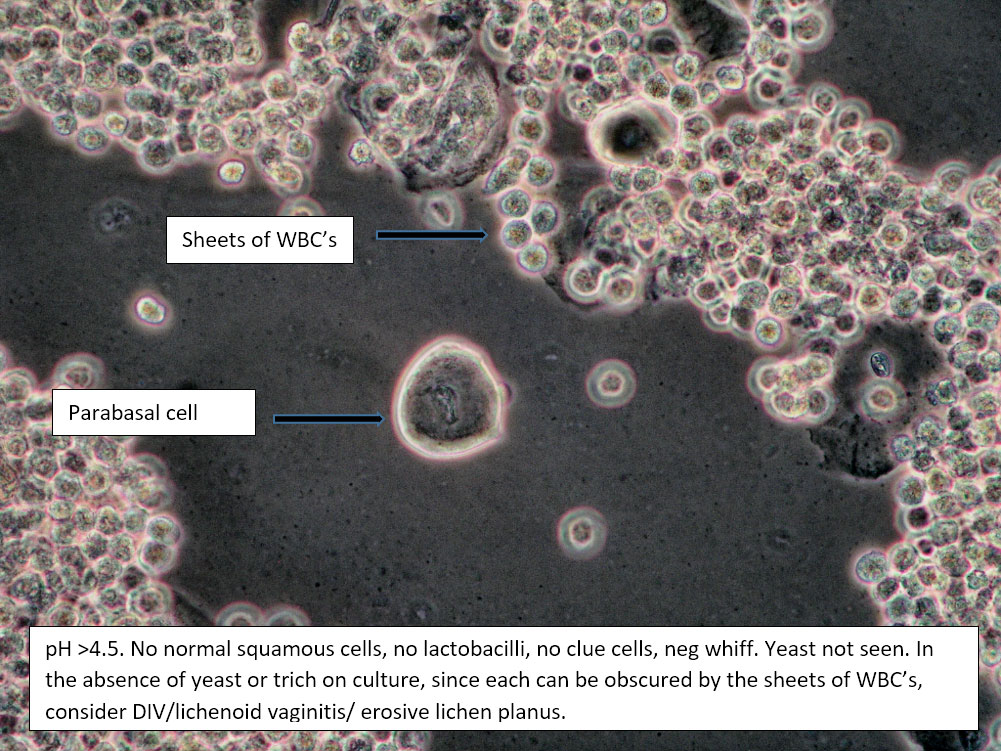
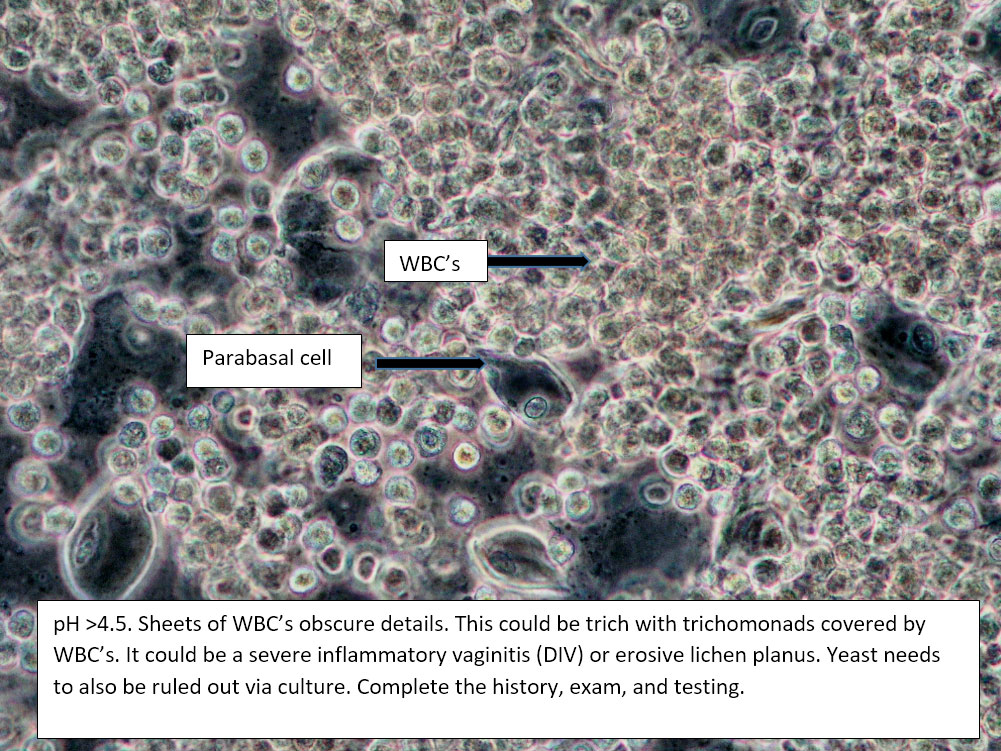
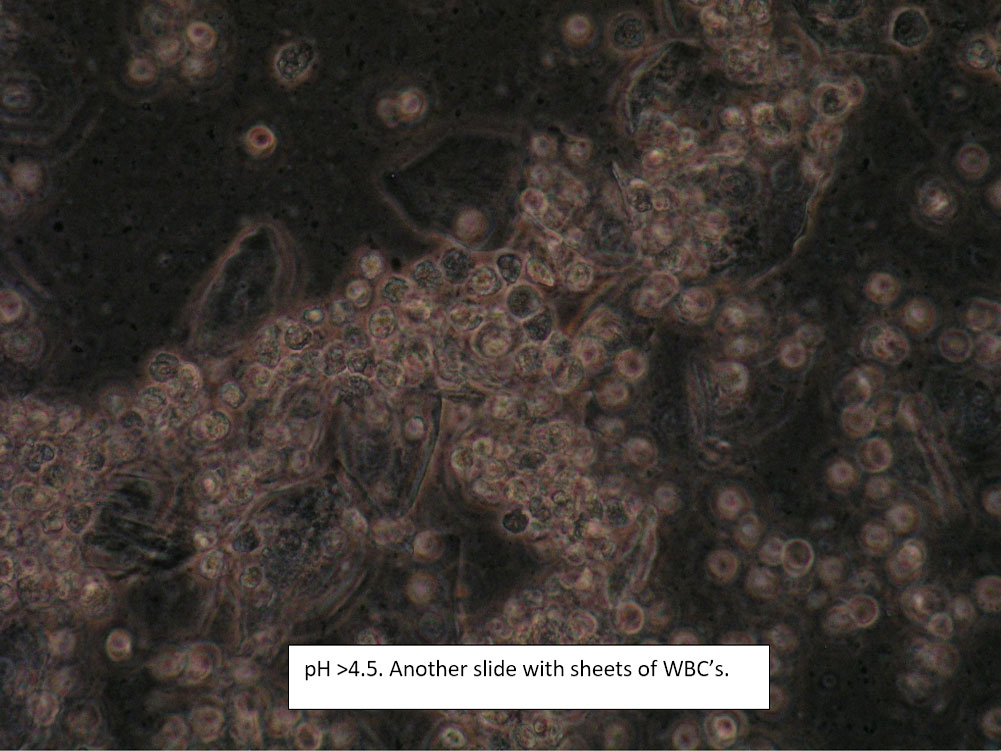
| Box 6: Sheets of white blood cells obscuring details |
1) Trichomonas 2) Yeast 3) Inflammatory vaginitis (DIV), erosive lichen planus 4) Upper tract disease |
1) Adjuvant test for trichomonas 2) Yeast culture 3) If trich and yeast tests are negative, treat for DIV. 4) (Atrophy is unlikely to present with so many WBCs). 5) Consider upper tract disease 6) Complete Algorithm steps |
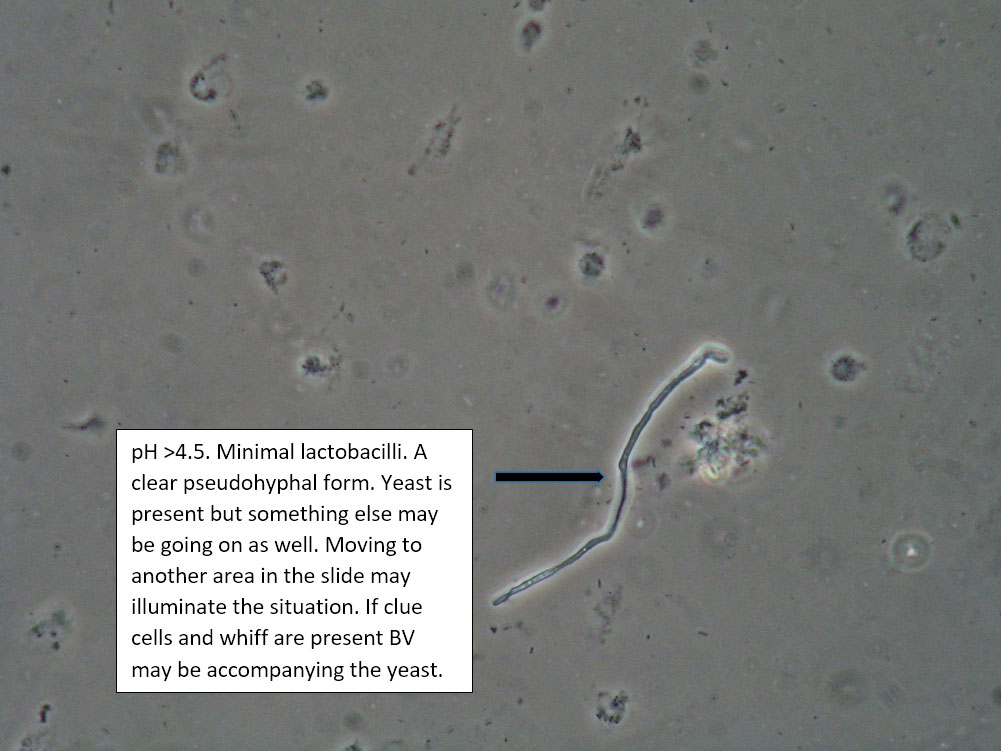
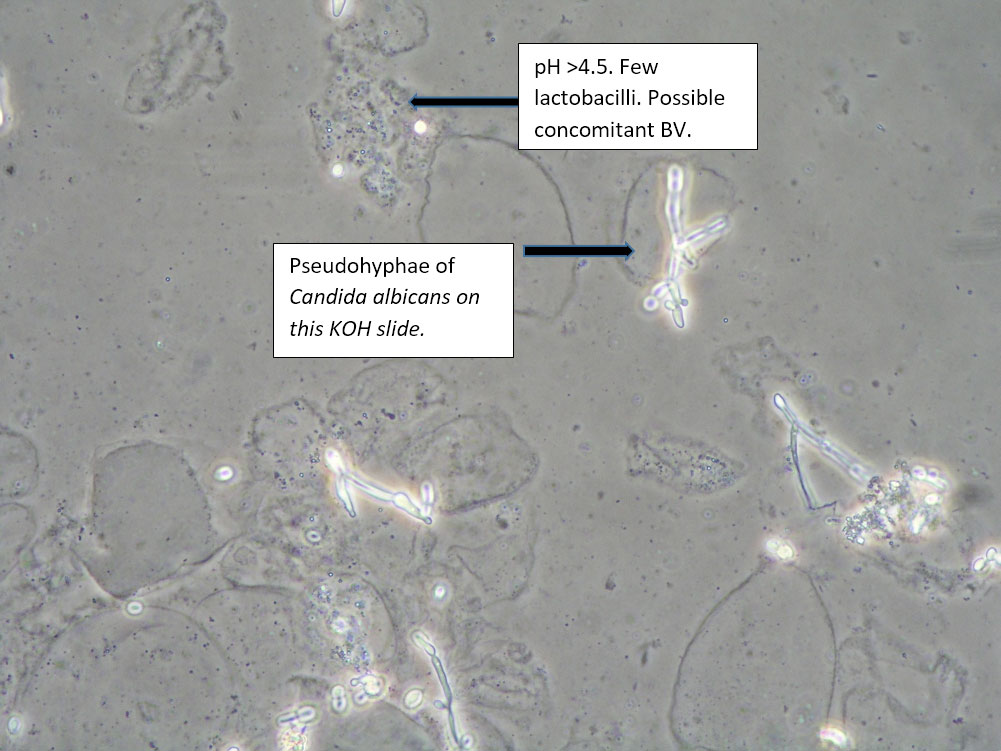
| Box 7: Any of the above configurations with KOH positive for hyphae and budding spores |
Mixed disorder with Candida | 1) Treat for yeast 2) Treat for concomitant conditions. 3) Complete Algorithm steps |
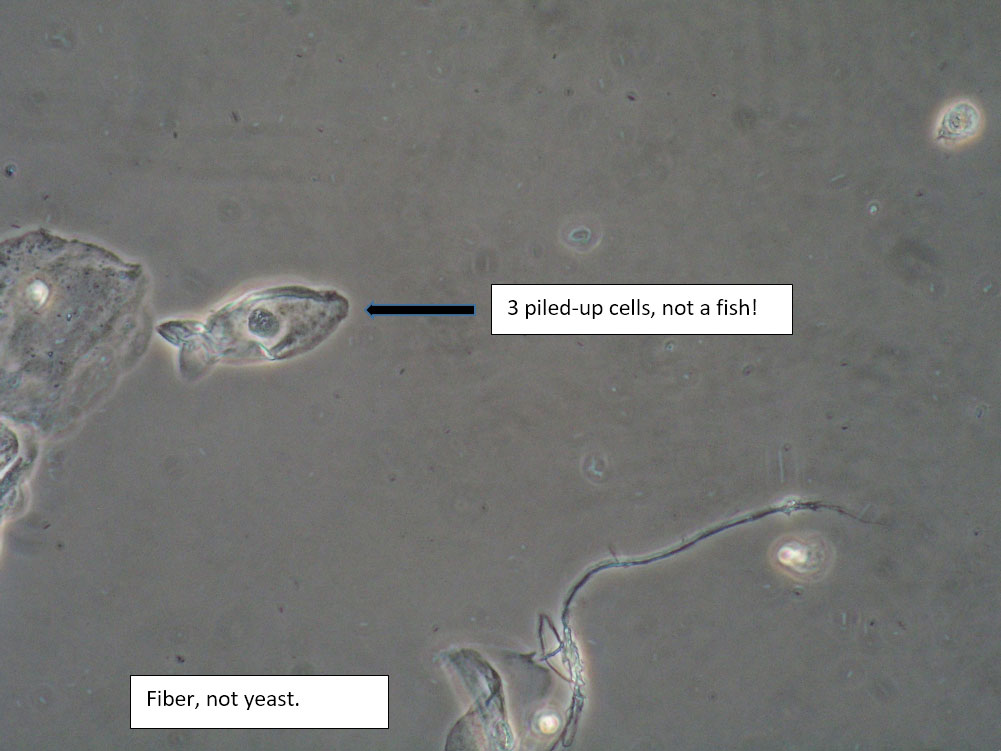
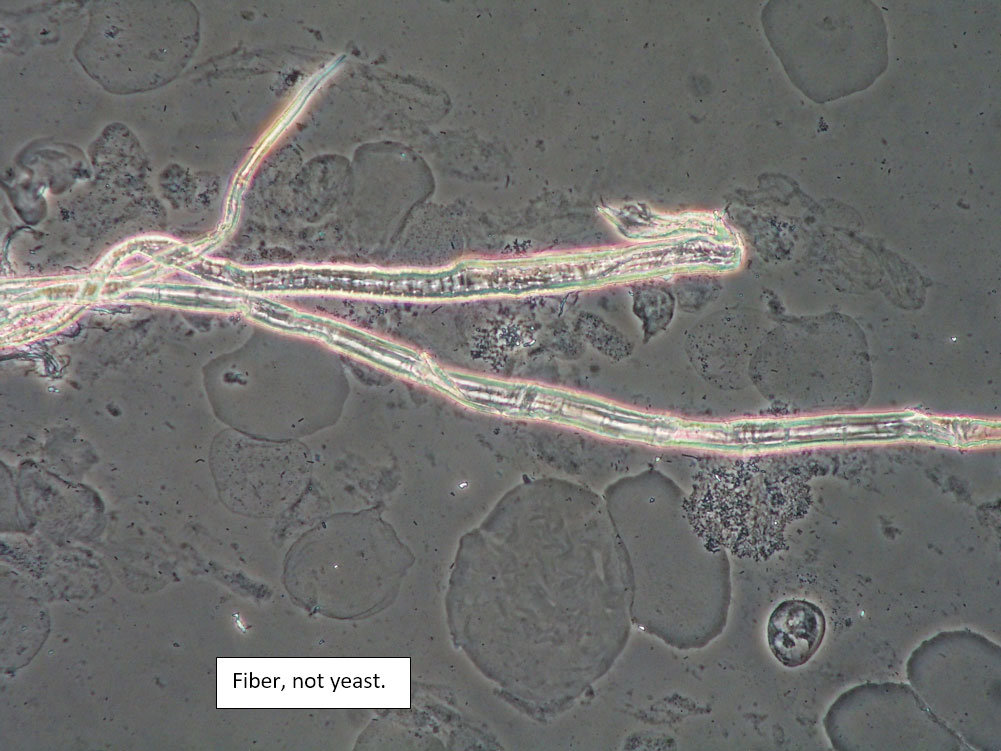
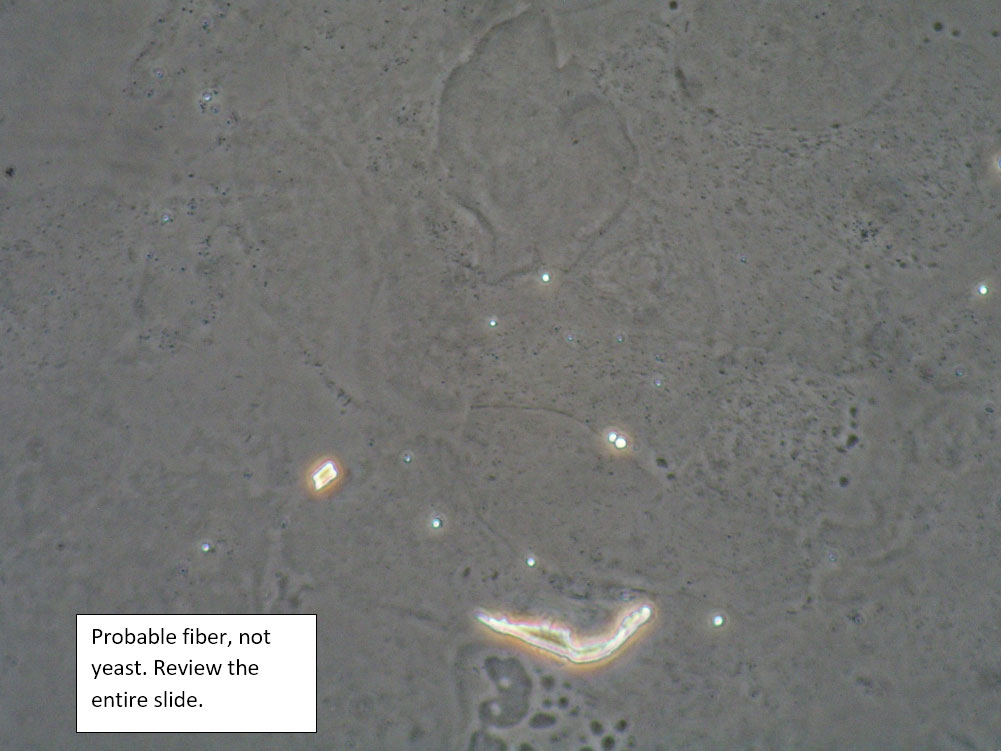
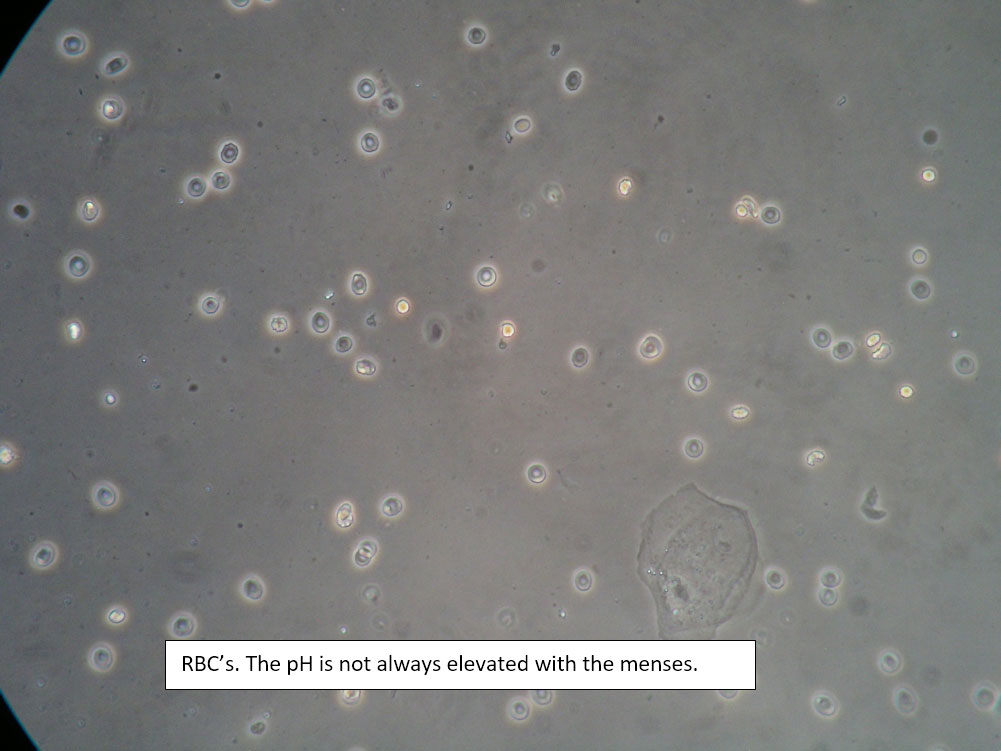
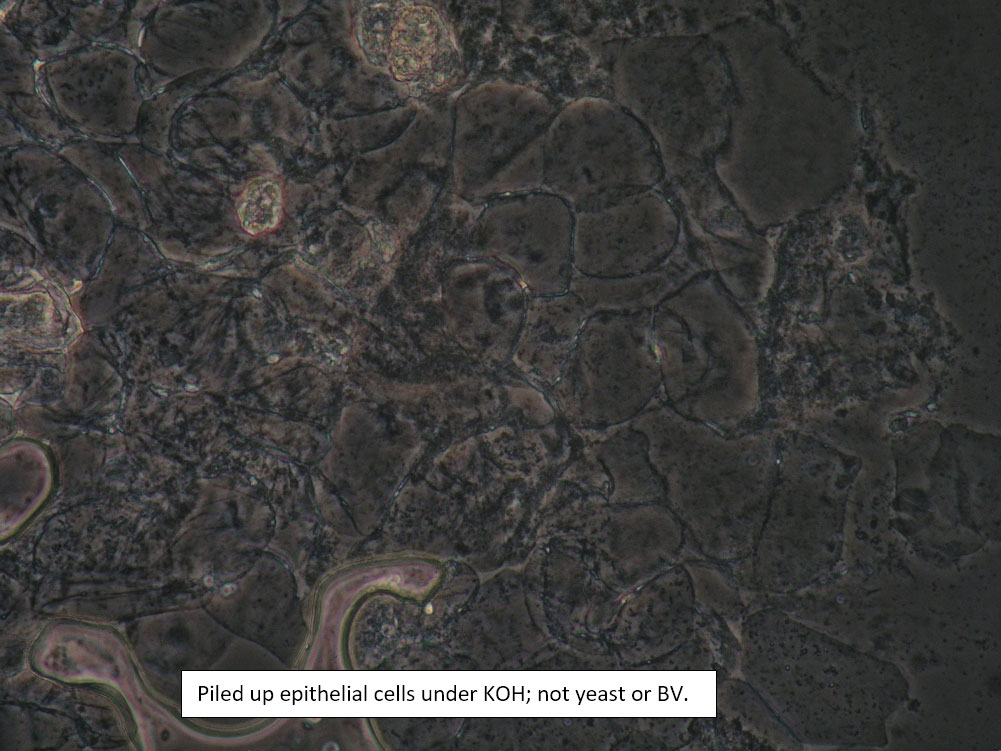
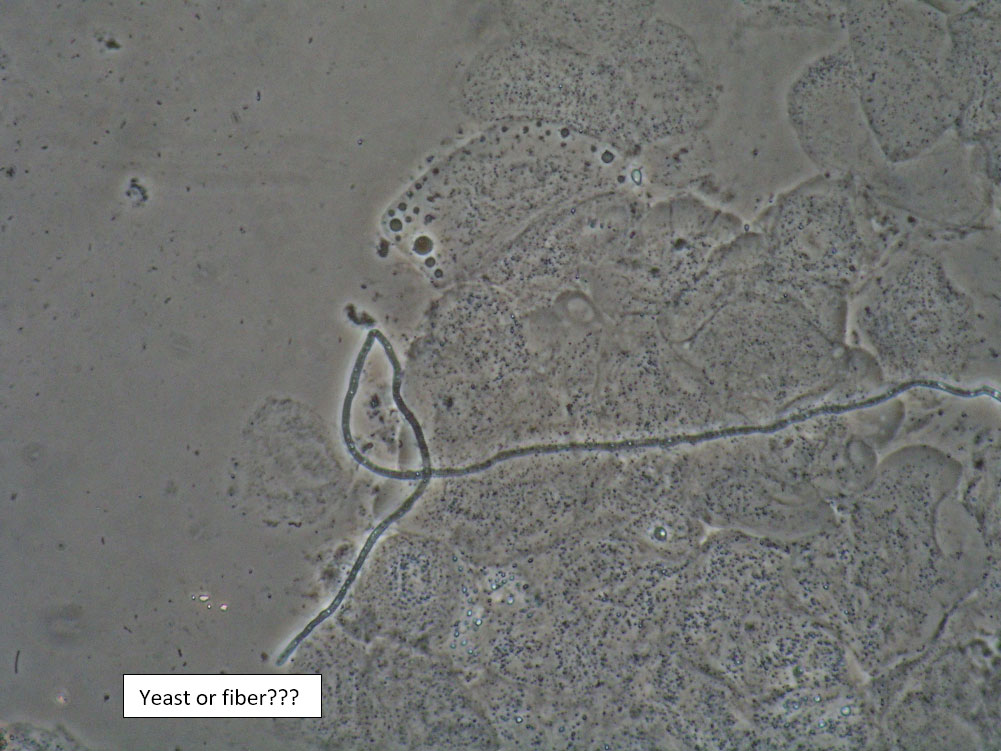
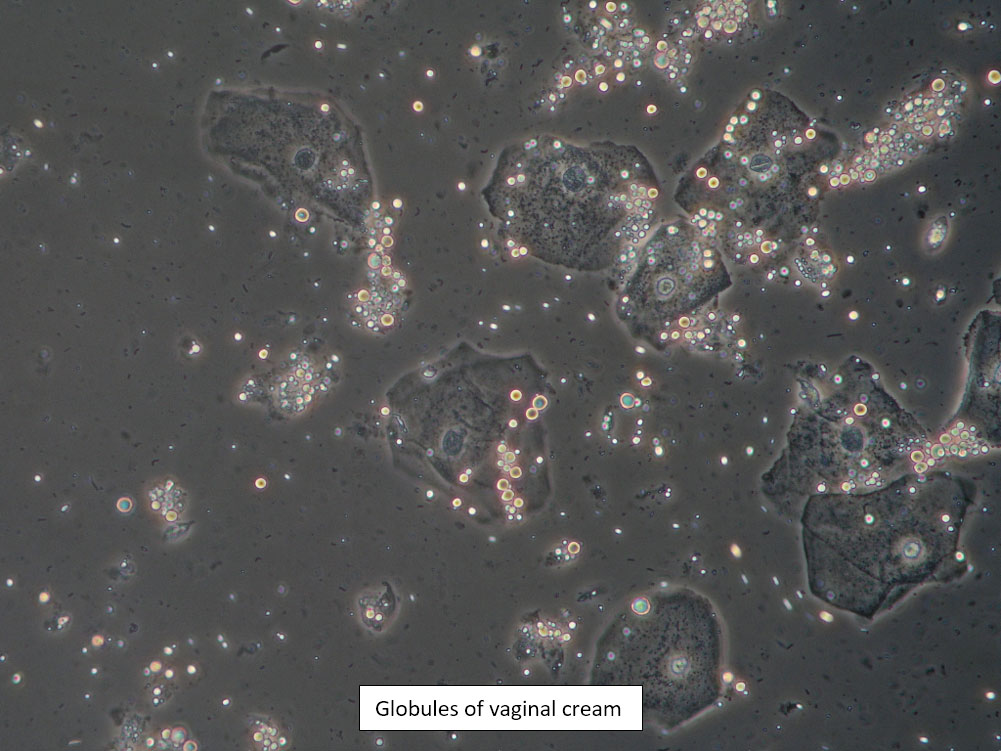
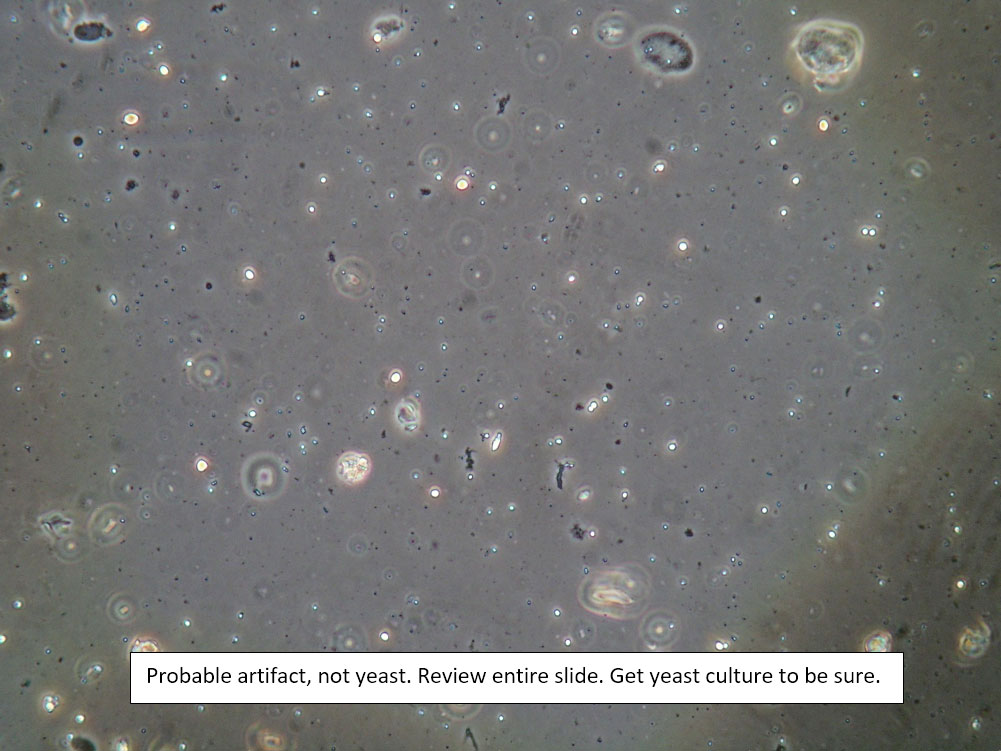
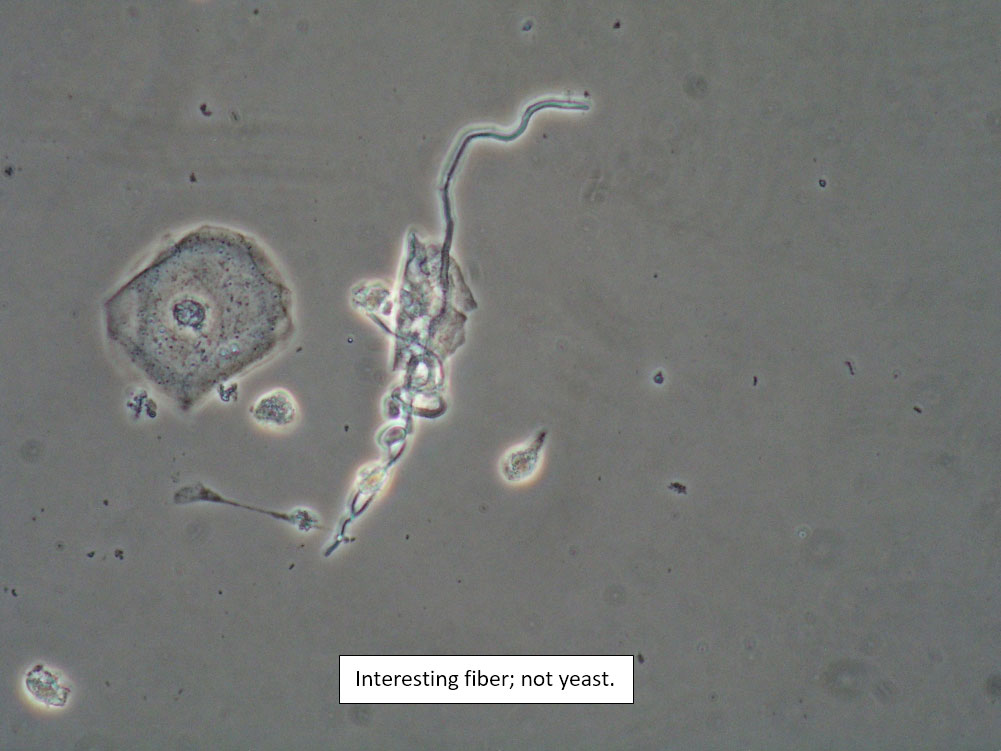
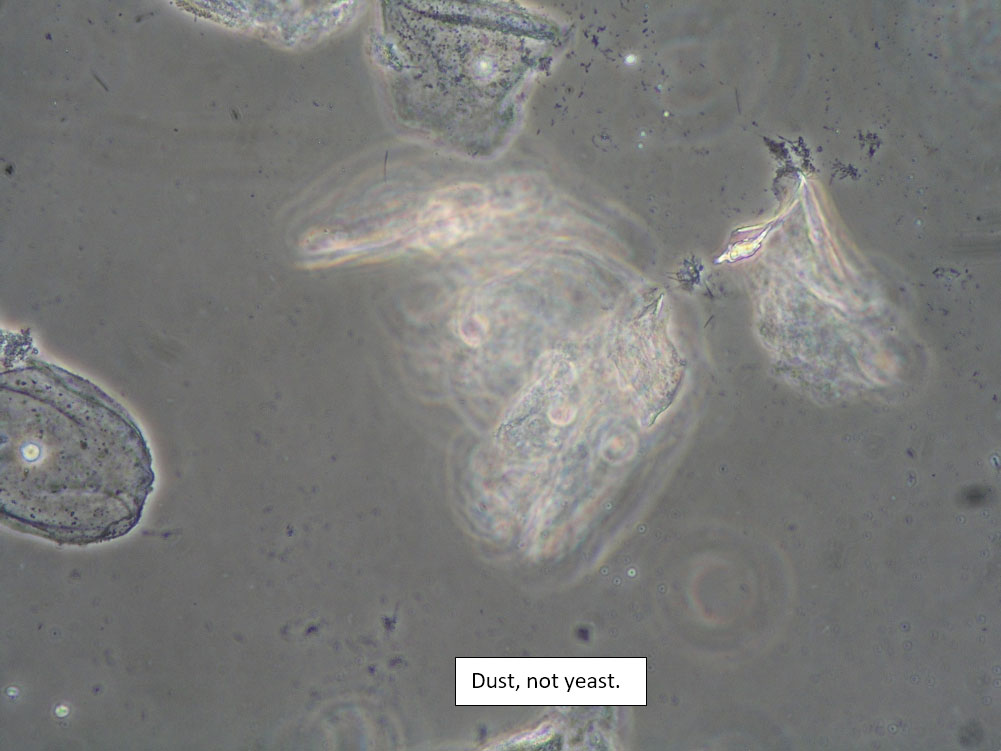
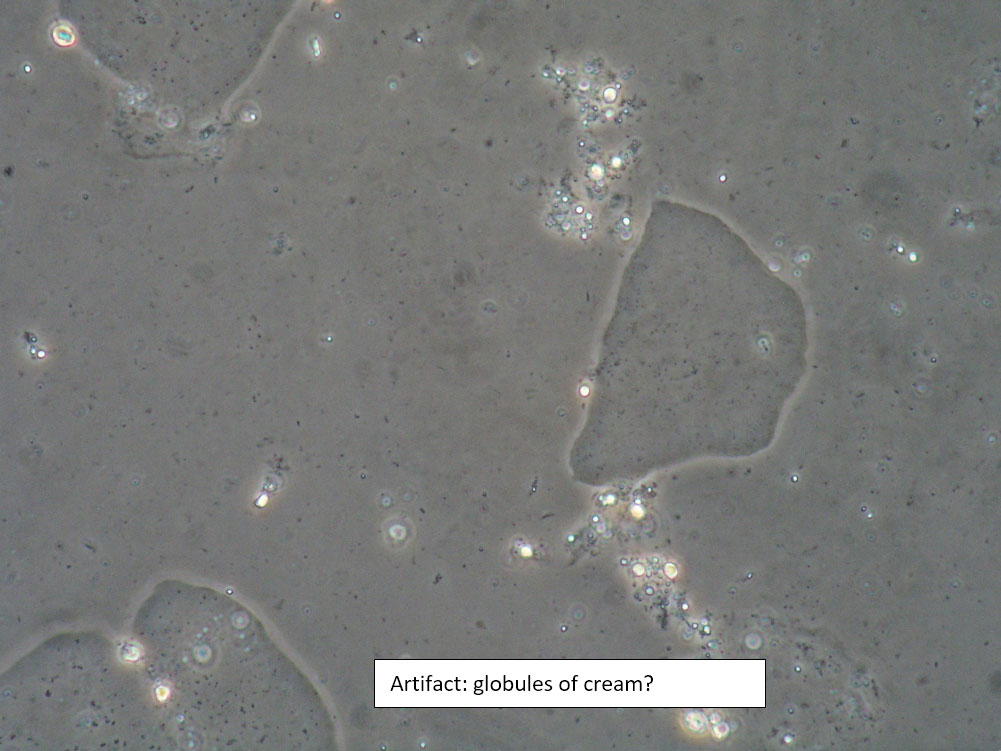
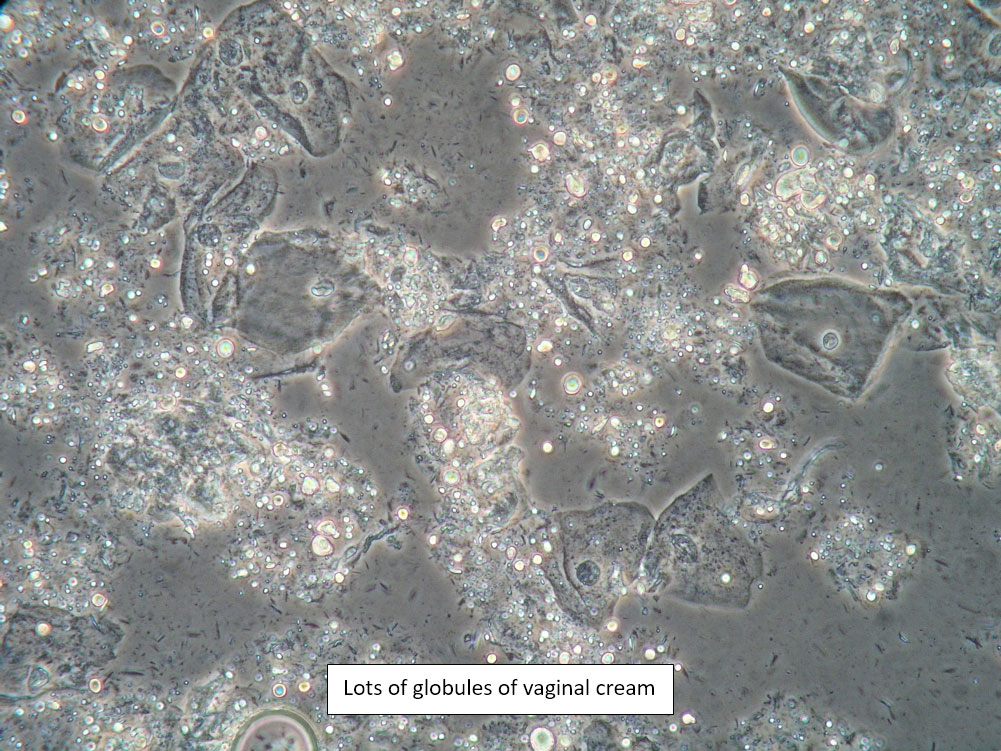
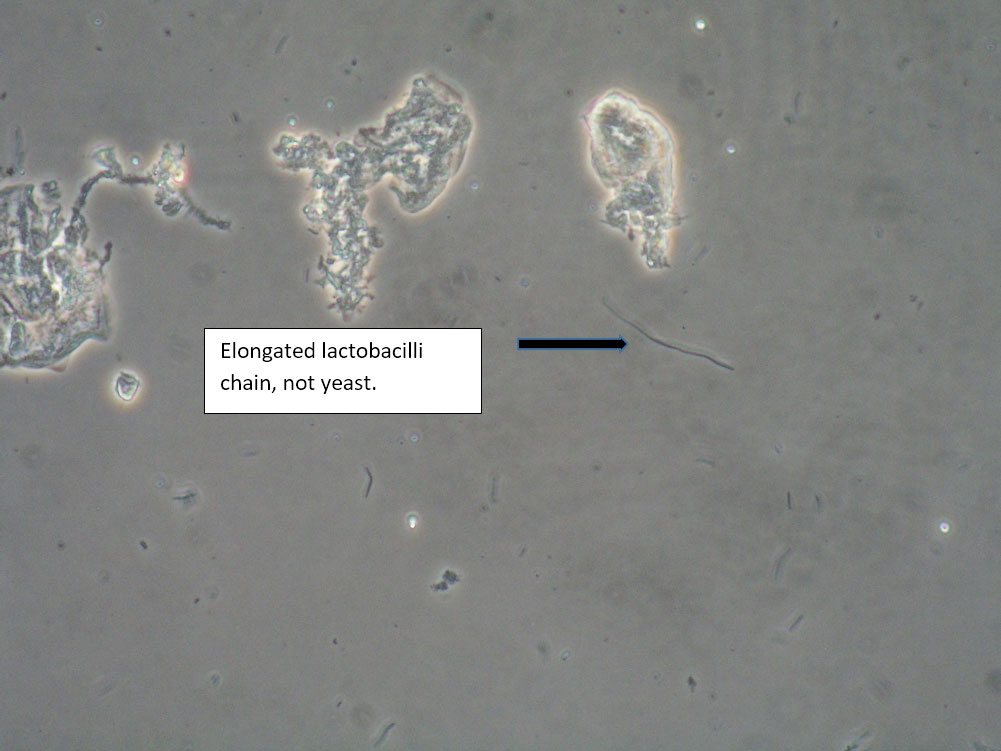
| Box 8: Any of the above configurations may include globules of creams being used, dust, fibers from a Q-tip, and other types of artifact. Red blood cells may also be seen. |
Artifact Red blood cells. |
Be sure not to be misled by artifact that can look like spores, hyphae, lactobacilli, or clue cells, etc. |